Mechanism of fibrotic cardiomyopathy in mice expressing truncated Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1
- PMID: 22278938
- PMCID: PMC3336781
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-201319
Mechanism of fibrotic cardiomyopathy in mice expressing truncated Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1
Abstract
We have previously found that in failing human hearts, Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) is processed by caspase-3 into an active isoform, ROCKΔ1. The purpose of the current investigation was to elucidate the pathological consequences of truncated ROCK1 accumulation in the heart, the associated molecular mechanism of ROCKΔ1-mediated cardiac phenotype, and the molecular signaling between Rho kinase activation in cardiomyocytes and extracellular matrix response. We generated transgenic mice expressing ROCKΔ1 in cardiomyocytes to mimic the situation observed in human heart disease, whereas an additional kinase-deficient mouse was generated as a control. The ROCKΔ1 transgenic mice developed fibrotic cardiomyopathy with diastolic dysfunction. Transgenic hearts displayed activated TGFβ1 and NF-κB signaling and a release of a subset of cytokines and were susceptible to angiotensin II stress. Treatment with a Rho kinase inhibitor attenuated the fibrotic phenotype. Cardiac fibroblasts differentiated into myofibroblasts when cocultured with transgenic cardiomyocytes but not with wild-type cardiomyocytes. Inhibitors of Rho kinase as well as TGFβR1 and NF-κB decreased these effects. The serum response factor-dependent TGFβ1 regulation was shown to be responsible for the Rho kinase-mediated activation of TGFβ1 signaling. We conclude that ROCKΔ1 is a novel fibrotic factor. Activation of TGFβ1 and NF-κB signaling contributes to the Rho kinase-mediated pathological fibrosis.
Figures
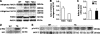


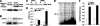




Similar articles
-
Osteoglycin attenuates cardiac fibrosis by suppressing cardiac myofibroblast proliferation and migration through antagonizing lysophosphatidic acid 3/matrix metalloproteinase 2/epidermal growth factor receptor signalling.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Apr 1;114(5):703-712. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy035. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29415171
-
ROCK2 regulates TGF-β-induced expression of CTGF and profibrotic genes via NF-κB and cytoskeleton dynamics in mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):F839-F851. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00596.2018. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31364374
-
Estradiol attenuates the TGF-β1-induced conversion of primary TAFs into myofibroblasts and inhibits collagen production and myofibroblast contraction by modulating the Smad and Rho/ROCK signaling pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Sep;36(3):801-7. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2288. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26179216
-
Coronary adventitial cells are linked to perivascular cardiac fibrosis via TGFβ1 signaling in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Oct;63:122-34. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23911435 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase (ROCK) in cardiovascular fibrosis and stiffening.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Jan;24(1):47-62. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1712593. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 31906742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of both ROCK1 and ROCK2 genes in cardiomyocytes promotes autophagy and reduces cardiac fibrosis during aging.FASEB J. 2019 Jun;33(6):7348-7362. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802510R. Epub 2019 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30848941 Free PMC article.
-
Rho Kinases in Embryonic Development and Stem Cell Research.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Jan 19;70(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00642-z. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 35043239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SLIT3 promotes cardiac fibrosis and differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts by RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(7):832-840. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.73812.16044. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38800023 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficient Rock1+/- and Rock2+/- Mice Are Not Protected from Cardiac Inflammation and Postinflammatory Fibrosis in Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis.Cells. 2020 Mar 12;9(3):700. doi: 10.3390/cells9030700. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32178482 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK1 deficiency preserves caveolar compartmentalization of signaling molecules and cell membrane integrity.FASEB Bioadv. 2024 Feb 23;6(3):85-102. doi: 10.1096/fba.2024-00015. eCollection 2024 Mar. FASEB Bioadv. 2024. PMID: 38463696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y. M., Bo J., Taffet G. E., Chang J., Shi J., Reddy A. K., Michael L. H., Schneider M. D., Entman M. L., Schwartz R. J., Wei L. (2006) Targeted deletion of ROCK1 protects the heart against pressure overload by inhibiting reactive fibrosis. FASEB J. 20, 916–925 - PubMed
-
- Sebbagh M., Renvoize C., Hamelin J., Riche N., Bertoglio J., Breard J. (2001) Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 346–352 - PubMed
-
- Coleman M. L., Sahai E. A., Yeo M., Bosch M., Dewar A., Olson M. F. (2001) Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 339–345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

