A novel EST-derived RNAi screen reveals a critical role for farnesyl diphosphate synthase in β2-adrenergic receptor internalization and down-regulation
- PMID: 22278941
- PMCID: PMC3336790
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-193870
A novel EST-derived RNAi screen reveals a critical role for farnesyl diphosphate synthase in β2-adrenergic receptor internalization and down-regulation
Abstract
The β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) plays important physiological roles in the heart and lung and is the primary target of β-agonists, the mainstay asthma drugs. Activation of β2AR by β-agonists is attenuated by receptor down-regulation, which ensures transient stimulation of the receptor but reduces the efficacy of β-agonists. Here we report the identification, through a functional genome-wide RNA interference (RNAi) screen, of new genes critically involved in β2AR down-regulation. We developed a lentivirus-based RNAi library consisting of 26-nt short-hairpin RNAs (shRNAs). The library was generated enzymatically from a large collection of expressed sequence tag (EST) DNAs corresponding to ∼20,000 human genes and contains on average ∼6 highly potent shRNAs (>75% knockdown efficiency) for each gene. Using this novel shRNA library, together with a robust cell model for β2AR expression, we performed fluorescence-activated cell sorting and isolated cells that, as a consequence of shRNA-mediated gene inactivation, exhibited defective agonist-induced down-regulation. The screen discovered several previously unrecognized β2AR regulators, including farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FDPS). We showed that inactivation of FDPS by shRNA, small interfering RNA, or the highly specific pharmaceutical inhibitor alendronate inhibited β2AR down-regulation. Notably, in human airway smooth muscle cells, the physiological target of β-agonists, alendronate treatment functionally reversed agonist-induced endogenous β2AR loss as indicated by an increase in cAMP production. FDPS inactivation interfered with β2AR internalization into endosomes through disrupting the membrane localization of the Rab5 small GTPase. Furthermore, Rab5 overexpression reversed the deficient receptor down-regulation induced by alendronate, suggesting that FDPS regulates receptor down-regulation in a Rab5-dependent manner. Together, our findings reveal a FDPS-dependent mechanism in the internalization and down-regulation of β2AR, identify FDPS as a potential target for improving the therapeutic efficacy of β-agonists, and demonstrate the utility of the unique EST-derived shRNA library for functional genetics studies.
Figures

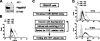

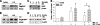

Similar articles
-
Role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in agonist-induced down-regulation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor.J Biol Chem. 1998 Mar 20;273(12):6976-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.12.6976. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9507004
-
A CREB-mediated increase in miRNA let-7f during prolonged β-agonist exposure: a novel mechanism of β2-adrenergic receptor down-regulation in airway smooth muscle.FASEB J. 2018 Jul;32(7):3680-3688. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701278R. Epub 2018 Feb 13. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29455573 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of pepducins as Gs-biased allosteric agonists.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 26;289(52):35668-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.618819. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25395624 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the Role of β2AR and TRPV1 in Respiratory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10234. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910234. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential benefits of therapeutic use of β2-adrenergic receptor agonists in neuroprotection and Parkinsonμs disease.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:103780. doi: 10.1155/2014/103780. Epub 2014 Jan 19. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24741572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of β-adrenergic receptor trafficking and lung microvascular endothelial cell permeability by Rab5 GTPase.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 1;11(8):868-78. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12045. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26157342 Free PMC article.
-
Rab5-mediated VE-cadherin internalization regulates the barrier function of the lung microvascular endothelium.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec;72(24):4849-66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1973-4. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26112597 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of alendronate on proteome of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.Int J Proteomics. 2014;2014:532953. doi: 10.1155/2014/532953. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Int J Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24653834 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 Nov;16(11):661-674. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0218-x. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31186539 Review.
-
Nebulization of risedronate alleviates airway obstruction and inflammation of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases via suppressing prenylation-dependent RAS/ERK/NF-κB and RhoA/ROCK1/MLCP signaling.Respir Res. 2022 Dec 28;23(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02274-5. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 36575527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson M. (1998) The beta-adrenoceptor. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 158, S146–153 - PubMed
-
- Pierce K. L., Premont R. T., Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 639–650 - PubMed
-
- Barnes P. J. (2004) New drugs for asthma. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 831–844 - PubMed
-
- Tattersfield A. E., Knox A. J., Britton J. R., Hall I. P. (2002) Asthma. Lancet 360, 1313–1322 - PubMed
-
- Dohlman H. G. (2002) Diminishing returns. Nature 418, 591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

