Anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 is essential for the development and sustained growth of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22279045
- PMCID: PMC3273836
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.182980.111
Anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 is essential for the development and sustained growth of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) frequently relapses after initial treatment. Drug resistance in AML has been attributed to high levels of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bcl-x(L) and Mcl-1. Here we report that removal of Mcl-1, but not loss or pharmacological blockade of Bcl-x(L), Bcl-2, or Bcl-w, caused the death of transformed AML and could cure disease in AML-afflicted mice. Enforced expression of selective inhibitors of prosurvival Bcl-2 family members revealed that Mcl-1 is critical for survival of human AML cells. Thus, targeting of Mcl-1 or regulators of its expression may be a useful strategy for the treatment of AML.
Figures
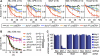
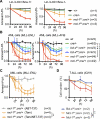
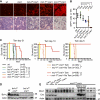
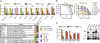
Comment in
-
Selectively targeting Mcl-1 for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia and solid tumors.Genes Dev. 2012 Feb 15;26(4):305-11. doi: 10.1101/gad.186189.111. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22345513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastassiadis K, Glaser S, Kranz A, Berhardt K, Stewart AF 2010. A practical summary of site-specific recombination, conditional mutagenesis, and tamoxifen induction of CreERT2. Methods Enzymol 477: 109–123 - PubMed
-
- Bouillet P, Robati M, Bath ML, Strasser A 2005. Polycystic kidney disease prevented by transgenic RNA interference. Cell Death Differ 12: 831–833 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
