The amplitude and timing of the BOLD signal reflects the relationship between local field potential power at different frequencies
- PMID: 22279224
- PMCID: PMC6796252
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3985-11.2012
The amplitude and timing of the BOLD signal reflects the relationship between local field potential power at different frequencies
Abstract
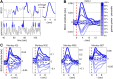
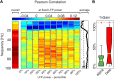
There is growing evidence that several components of the mass neural activity contributing to the local field potential (LFP) can be partly separated by decomposing the LFP into nonoverlapping frequency bands. Although the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signal has been found to correlate preferentially with specific frequency bands of the LFP, it is still unclear whether the BOLD signal relates to the activity expressed by each LFP band independently of the others or if, instead, it also reflects specific relationships among different bands. We investigated these issues by recording, simultaneously and with high spatiotemporal resolution, BOLD signal and LFP during spontaneous activity in early visual cortices of anesthetized monkeys (Macaca mulatta). We used information theory to characterize the statistical dependency between BOLD and LFP. We found that the alpha (8-12 Hz), beta (18-30 Hz), and gamma (40-100 Hz) LFP bands were informative about the BOLD signal. In agreement with previous studies, gamma was the most informative band. Both increases and decreases in BOLD signal reliably followed increases and decreases in gamma power. However, both alpha and beta power signals carried information about BOLD that was largely complementary to that carried by gamma power. In particular, the relationship between alpha and gamma power was reflected in the amplitude of the BOLD signal, while the relationship between beta and gamma bands was reflected in the latency of BOLD with respect to significant changes in gamma power. These results lay the basis for identifying contributions of different neural pathways to cortical processing using fMRI.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Stimulus-induced dissociation of neuronal firing rates and local field potential gamma power and its relationship to the resonance blood oxygen level-dependent signal in macaque primary visual cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Dec;34(11):1857-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07877.x. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22081989 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen Level and LFP in Task-Positive and Task-Negative Areas: Bridging BOLD fMRI and Electrophysiology.Cereb Cortex. 2016 Jan;26(1):346-57. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu260. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Cereb Cortex. 2016. PMID: 25385710 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in BOLD transients with visual stimuli across 1-44 Hz.Neurosci Lett. 2008 May 9;436(2):185-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.021. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Neurosci Lett. 2008. PMID: 18400397
-
The neural basis of the blood-oxygen-level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging signal.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002 Aug 29;357(1424):1003-37. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2002.1114. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12217171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How and when the fMRI BOLD signal relates to underlying neural activity: the danger in dissociation.Brain Res Rev. 2010 Mar;62(2):233-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Brain Res Rev. 2010. PMID: 20026191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A multivariate comparison of electroencephalogram and functional magnetic resonance imaging to electrocorticogram using visual object representations in humans.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 18;16:983602. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.983602. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36330341 Free PMC article.
-
A neurodynamic model of inter-brain coupling in the gamma band.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Nov 1;128(5):1085-1090. doi: 10.1152/jn.00224.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 36070245 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent approaches toward the study of multisensory perception.Front Syst Neurosci. 2013 Nov 8;7:81. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00081. eCollection 2013. Front Syst Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24265607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationships between correlated spikes, oxygen and LFP in the resting-state primate.Neuroimage. 2022 Feb 15;247:118728. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118728. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2022. PMID: 34923136 Free PMC article.
-
The fusion of mental imagery and sensation in the temporal association cortex.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 8;34(41):13684-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0943-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25297095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basar E. EEG-brain dynamics: relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials. Amsterdam: Elsevier-North-Holland Biomedical; 1980.
-
- Brown GG, Perthen JE, Liu TT, Buxton RB. A primer on functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007;17:107–125. - PubMed
-
- Brunel N, Wang XJ. What determines the frequency of fast network oscillations with irregular neural discharges? I. Synaptic dynamics and excitation-inhibition balance. J Neurophysiol. 2003;90:415–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
