Systematic review of herbals as potential anti-inflammatory agents: Recent advances, current clinical status and future perspectives
- PMID: 22279370
- PMCID: PMC3263046
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-7847.91102
Systematic review of herbals as potential anti-inflammatory agents: Recent advances, current clinical status and future perspectives
Abstract
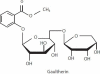
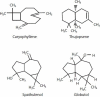
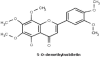
Many synthetic drugs reported to be used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders are of least interest now a days due to their potential side effects and serious adverse effects and as they are found to be highly unsafe for human assistance. Since the last few decades, herbal drugs have regained their popularity in treatment against several human ailments. Herbals containing anti-inflammatory activity (AIA) are topics of immense interest due to the absence of several problems in them, which are associated with synthetic preparations. The primary objective of this review is to provide a deep overview of the recently explored anti-inflammatory agents belonging to various classes of phytoconstituents like alkaloids, glycosides, terpenoids, steroids, polyphenolic compounds, and also the compounds isolated from plants of marine origin, algae and fungi. Also, it enlists a distended view on potential interactions between herbals and synthetic preparations, related adverse effects and clinical trials done on herbals for exploring their AIA. The basic aim of this review is to give updated knowledge regarding plants which will be valuable for the scientists working in the field of anti-inflammatory natural chemistry.
Keywords: Alkaloids; anti-inflammatory agents; cannabinoids; clinical trials; glycosides; herbals; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
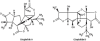
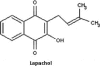
Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Herbs with Special Emphasis on Herbal Medicines for Countering Inflammatory Diseases and Disorders - A Review.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2018;12(1):39-58. doi: 10.2174/1872213X12666180115153635. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29336271 Review.
-
Recent advancements in the development of heterocyclic anti-inflammatory agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Aug 15;200:112438. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112438. Epub 2020 May 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32485533 Review.
-
Marine Alkaloids with Anti-Inflammatory Activity: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Mar Drugs. 2020 Mar 2;18(3):147. doi: 10.3390/md18030147. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32121638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential anti-inflammatory natural products from marine algae.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;48:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.023. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27716532 Review.
-
A review of the ethnomedicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacological properties of the genus Acanthus (Acanthaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115271. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115271. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35430290 Review.
Cited by
-
Rediscovering the Therapeutic Potential of Agarwood in the Management of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Molecules. 2022 May 9;27(9):3038. doi: 10.3390/molecules27093038. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 26;12(9):2586. doi: 10.3390/nu12092586. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32858855 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of nanotechnology and experimental design in the development and optimization of a posaconazole‒calendula oil nanoemulgel for the treatment of mouth disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1347551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1347551. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38434704 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Inflammatory Response to Implanted Biomaterials Using Natural Compounds.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(41):6347-6357. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170510124348. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28521709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploitation of capsule system for colon targeted drug delivery of biopolymer-based microparticles: in vivo and in vitro applications.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 4;8(11):e11390. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11390. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36387434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denko CW. A role of neuropeptides in inflammation. In: Whicher JT, Evans SW, editors. Biochemistry of inflammation. London: Kluwer Publisher; 1992. pp. 177–81.
-
- Singh A, Malhotra S, Subban R. Anti inflammatory and analgesic agents from Indian medicinal plants. Int J Integ Biol. 2008;3:57–72.
-
- Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: The beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1191–7. - PubMed
-
- Collins CK. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company; 1998.
-
- Bottazzi B, Doni A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A. An integrated view of humoral innate immunity: Pentraxins as a paradigm. Ann Rev Immunol. 2010;28:157–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
