Synovial Tissue Response to Treatment with TNF Blockers in Peripheral Spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 22279512
- PMCID: PMC3263444
- DOI: 10.2174/1874312901105010127
Synovial Tissue Response to Treatment with TNF Blockers in Peripheral Spondyloarthritis
Abstract
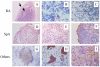
This review describes the synovial response to treatment in peripheral spondyloarthritis (SpA). A series of recent studies demonstrates that the synovial histopathology is largely homogenous between different SpA subtypes and can be strongly modulated by effective treatment such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockade. This includes a dramatic reduction of the infiltration with inflammatory cells (with the intriguing exception of B lymphocytes and plasma cells), a modulation of structural features such as vascularity, intimal lining layer hyperplasia, and ectopic lymphoid neogenesis, and a down-regulation of a variety of mediators involved in tissue damage. The analysis of tissue response to targeted therapies appears to be a novel and elegant approach to study the immunopathology of human peripheral SpA in vivo. Moreover, detailed cellular and molecular analysis of synovial features allows to identify synovial biomarkers of clinical response to therapeutic interventions which can be used in future early phase clinical trials in SpA.
Keywords: Spondyloarthritis; Synovial biomarkers.; Synovial tissue; TNF blockade.
Figures
References
-
- Vanden Bosch F, Kruithof E, Baeten D, et al. Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) versus placebo in active spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:755–65. - PubMed
-
- Brandt J, Haibel H, Cornely D, et al. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1346–52. - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1187–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
