A new model for raf kinase inhibitory protein induced chemotherapeutic resistance
- PMID: 22279539
- PMCID: PMC3261143
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029532
A new model for raf kinase inhibitory protein induced chemotherapeutic resistance
Abstract
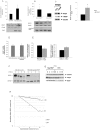
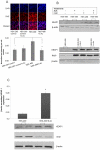
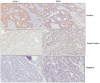
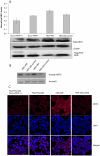
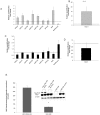
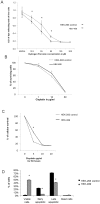
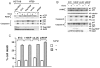
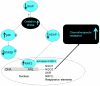
Therapeutic resistance remains the most challenging aspect of treating cancer. Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) emerged as a molecule capable of sensitizing cancerous cells to radio- and chemotherapy. Moreover, this small evolutionary conserved molecule, endows significant resistance to cancer therapy when its expression is reduced or lost. RKIP has been shown to inhibit the Raf-MEK-ERK, NFκB, GRK and activate the GSK3β signaling pathways. Inhibition of Raf-MEK-ERK and NFκB remains the most prominent pathways implicated in the sensitization of cells to therapeutic drugs. Our purpose was to identify a possible link between RKIP-KEAP 1-NRF2 and drug resistance. To that end, RKIP-KEAP 1 association was tested in human colorectal cancer tissues using immunohistochemistry. RKIP miRNA silencing and its inducible overexpression were employed in HEK-293 immortalized cells, HT29 and HCT116 colon cancer cell lines to further investigate our aim. We show that RKIP enhanced Kelch-like ECH-associated protein1 (KEAP 1) stability in colorectal cancer tissues and HT29 CRC cell line. RKIP silencing in immortalized HEK-293 cells (termed HEK-499) correlated significantly with KEAP 1 protein degradation and subsequent NRF2 addiction in these cells. Moreover, RKIP depletion in HEK-499, compared to control cells, bestowed resistance to supra physiological levels of H(2)O(2) and Cisplatin possibly by upregulating NF-E2-related nuclear factor 2 (NRF2) responsive genes. Similarly, we observed a direct correlation between the extent of apoptosis, after treatment with Adriamycin, and the expression levels of RKIP/KEAP 1 in HT29 but not in HCT116 CRC cells. Our data illuminate, for the first time, the NRF2-KEAP 1 pathway as a possible target for personalized therapeutic intervention in RKIP depleted cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Behbehani AI, Bitar MS, George SS, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in a survival analysis of colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5672–5679. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Tang CE, Ouyang GL, Ruan L, Li MY, et al. Identification of RKIP as a differentially tyrosine-phosphorylated protein in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and normal nasopharyngeal epithelial tissues by phosphoproteomic approach. Med Oncol. 2009;26:463–470. - PubMed
-
- Fu Z, Kitagawa Y, Shen R, Shah R, Mehra R, et al. Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate. 2006;66:248–256. - PubMed
-
- Hagan S, Al-Mulla F, Mallon E, Oien K, Ferrier R, et al. Reduction of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7392–7397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

