Circulating angiopoietin-2 as a biomarker in ANCA-associated vasculitis
- PMID: 22279570
- PMCID: PMC3261176
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030197
Circulating angiopoietin-2 as a biomarker in ANCA-associated vasculitis
Abstract
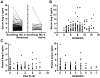
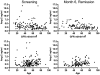
The endothelial-specific Angiopoietin-Tie2 ligand-receptor system is an important regulator of endothelial activation. Binding of angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) to Tie2 receptor renders the endothelial barrier responsive to pro-inflammatory cytokines. We previously showed that circulating Ang-2 correlated with disease severity in a small cohort of critically ill patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated glomerulonephritis. The current study reassessed Ang-2 as a biomarker of disease activity and relapse in AAV. Circulating Ang-2 was measured in 162 patients with severe AAV (BVAS/WG≥3, with or without glomerulonephritis) in a clinical trial. Ang-2 levels during active AAV were compared to levels in the same patients during remission (BVAS/WG = 0). Levels in clinical subsets of AAV were compared, and association with future disease course was assessed. Ang-2 levels were elevated in severe disease (median 3.0 ng/ml, interquartile range 1.9-4.4) compared to healthy controls (1.2, 0.9-1.5). However, they did not reliably decline with successful treatment (median 2.6 ng/ml, interquartile range 1.9-3.8, median change -0.1). Ang-2 correlated weakly with BVAS/WG score (r = 0.17), moderately with markers of systemic inflammation (r = 0.25-0.41), and inversely with renal function (r = -0.36). Levels were higher in patients with glomerulonephritis, but levels adjusted for renal dysfunction were no different in patients with or without glomerulonephritis. Levels were higher in patients with newly diagnosed AAV and lower in patients in whom treatment had recently been started. Ang-2 levels during active disease did not predict response to treatment, and Ang-2 levels in remission did not predict time to flare. Thus, Ang-2 appears to have limited practical value in AAV as a biomarker of disease activity at time of measurement or for predicting future activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kerr GS, Fleisher TA, Hallahan CW, Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, et al. Limited prognostic value of changes in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody titer in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Kyndt X, Reumaux D, Bridoux F, Tribout B, Bataille P, et al. Serial measurements of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in patients with systemic vasculitis. Am J Med. 1999;106:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Boomsma MM, Stegeman CA, van der Leij MJ, Oost W, Hermans J, et al. Prediction of relapses in Wegener's granulomatosis by measurement of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody levels: a prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2025–2033. - PubMed
-
- Girard T, Mahr A, Noel LH, Cordier JF, Lesavre P, et al. Are antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies a marker predictive of relapse in Wegener's granulomatosis? A prospective study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001;40:147–151. - PubMed
-
- Finkielman JD, Merkel PA, Schroeder D, Hoffman GS, Spiera R, et al. Antiproteinase 3 antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and disease activity in Wegener granulomatosis. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:611–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR024150-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR02224/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR052820/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000533/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR047785/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019497/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AR057319/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54AR057319/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058303/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI015416/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002224/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS064808/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RR 025771/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS064808/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00533/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR049185/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

