Rapid evaluation in whole blood culture of regimens for XDR-TB containing PNU-100480 (sutezolid), TMC207, PA-824, SQ109, and pyrazinamide
- PMID: 22279595
- PMCID: PMC3261206
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030479
Rapid evaluation in whole blood culture of regimens for XDR-TB containing PNU-100480 (sutezolid), TMC207, PA-824, SQ109, and pyrazinamide
Abstract
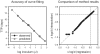
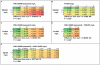
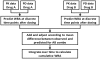
There presently is no rapid method to assess the bactericidal activity of new regimens for tuberculosis. This study examined PNU-100480, TMC207, PA-824, SQ109, and pyrazinamide, singly and in various combinations, against intracellular M. tuberculosis, using whole blood culture (WBA). The addition of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D facilitated detection of the activity of TMC207 in the 3-day cultures. Pyrazinamide failed to show significant activity against a PZA-resistant strain (M. bovis BCG), and was not further considered. Low, mid, and high therapeutic concentrations of each remaining drug were tested individually and in a paired checkerboard fashion. Observed bactericidal activity was compared to that predicted by the sum of the effects of individual drugs. Combinations of PNU-100480, TMC207, and SQ109 were fully additive, whereas those including PA-824 were less than additive or antagonistic. The cumulative activities of 2, 3, and 4 drug combinations were predicted based on the observed concentration-activity relationship, published pharmacokinetic data, and, for PNU-100480, published WBA data after oral dosing. The most active regimens, including PNU-100480, TMC207, and SQ109, were predicted to have cumulative activity comparable to standard TB therapy. Further testing of regimens including these compounds is warranted. Measurement of whole blood bactericidal activity can accelerate the development of novel TB regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro interactions between new antitubercular drug candidates SQ109 and TMC207.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jul;54(7):2840-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01601-09. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20385864 Free PMC article.
-
SQ109 and PNU-100480 interact to kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 May;67(5):1163-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr589. Epub 2012 Jan 17. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22258923
-
Sterilizing activity of novel TMC207- and PA-824-containing regimens in a murine model of tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Dec;55(12):5485-92. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05293-11. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21930883 Free PMC article.
-
New anti-tuberculosis drugs with novel mechanisms of action.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(19):1956-67. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132906. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18691051 Review.
-
Novel drugs against tuberculosis: a clinician's perspective.Eur Respir J. 2015 Apr;45(4):1119-31. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00162314. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Eur Respir J. 2015. PMID: 25431273 Review.
Cited by
-
Pipeline of drugs for related diseases: tuberculosis.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013 Nov;8(6):579-85. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000009. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013. PMID: 24100880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Increasing Concentrations of Rifampicin on Different Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lineages in a Whole-Blood Bactericidal Activity Assay.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Feb 15;66(2):e0169921. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01699-21. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34871090 Free PMC article.
-
Principles for designing future regimens for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.Bull World Health Organ. 2014 Jan 1;92(1):68-74. doi: 10.2471/BLT.13.122028. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Bull World Health Organ. 2014. PMID: 24391302 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of selective immune-cell depletion on growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) in a whole-blood bactericidal activity (WBA) assay.PLoS One. 2019 May 17;14(5):e0216616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216616. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31100071 Free PMC article.
-
Sterilizing activities of novel combinations lacking first- and second-line drugs in a murine model of tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jun;56(6):3114-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00384-12. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22470112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caminero JA, Sotgiu G, Zumla A, Migliori GB. Best drug treatment for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10:621–629. - PubMed
-
- Kim KS, Bayer AS. Significance of in-vitro penicillin tolerance in experimental enterococcal endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987;19:475–485. - PubMed
-
- Tuomanen E. Phenotypic tolerance: the search for beta-lactam antibiotics that kill nongrowing bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1986;8(Suppl 3):S279–S291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

