Dual function of Sec16B: Endoplasmic reticulum-derived protein secretion and peroxisome biogenesis in mammalian cells
- PMID: 22279616
- PMCID: PMC3265929
- DOI: 10.4161/cl.1.4.18341
Dual function of Sec16B: Endoplasmic reticulum-derived protein secretion and peroxisome biogenesis in mammalian cells
Abstract
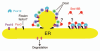
The origin of peroxisomes has long been disputed. However, recent evidence suggests that peroxisomes can be formed de novo from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in yeast and higher eukaryotes. Sec16A and Sec16B, mammalian orthologs of yeast Sec16, are scaffold proteins that organize ER exit sites by interacting with COPII components. We recently demonstrated that Sec16B, but not Sec16A, regulates the transport of peroxisomal biogenesis factors from the ER to peroxisomes in mammalian cells. The C-terminal region of Sec16B, which is not conserved in Sec16A, is required for this function. The data suggest that Sec16B in ER areas other than ER exit sites plays this role. Our findings provide an unexpected connection between at least part of the COPII machinery and the formation of preperoxisomal vesicles at the ER, and offer an explanation of how secretory and peroxisomal trafficking from the ER are distinguished.
Figures
Comment on
-
Sec16B is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum export of the peroxisomal membrane biogenesis factor peroxin 16 (Pex16) in mammalian cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 2;108(31):12746-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103283108. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21768384 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
