Skp2 is a promising therapeutic target in breast cancer
- PMID: 22279619
- PMCID: PMC3263529
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2011.00057
Skp2 is a promising therapeutic target in breast cancer
Abstract
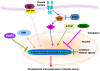
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer among American women, and remains the second leading cause of cancer-related death for female in the United States. It has been known that several signaling pathways and various factors play critical roles in the development and progression of breast cancer, such as estrogen receptor, Notch, PTEN, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, PI3K/Akt, BRCA1, and BRCA2. Emerging evidence has shown that the F-box protein S-phase kinase associated protein 2 (Skp2) also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Therefore, in this brief review, we summarize the novel functions of Skp2 in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Moreover, we provide further evidence regarding the state of our knowledge toward the development of novel Skp2 inhibitors especially natural "chemopreventive agents" as targeted approach for the prevention and/or treatment of breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Skp2: a novel potential therapeutic target for prostate cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1825(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.09.002. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21963805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose, quercetin, curcumin and lycopene induce cell-cycle arrest in MDA-MB-231 and BT474 cells through downregulation of Skp2 protein.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jun 22;59(12):6765-75. doi: 10.1021/jf201096v. Epub 2011 May 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21598989
-
The expression and prognosis of Emi1 and Skp2 in breast carcinoma: associated with PI3K/Akt pathway and cell proliferation.Med Oncol. 2013 Dec;30(4):735. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0735-0. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24277465
-
USP18 promotes breast cancer growth by upregulating EGFR and activating the AKT/Skp2 pathway.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):371-383. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4387. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29749454
-
Role of Notch signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Feb 1;7(2):173-186. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28337369 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Next generation sequencing and functional pathway analysis to understand the mechanism of action of copper-tolfenamic acid against pancreatic cancer cells.Process Biochem. 2020 Feb;89:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.022. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Process Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32719579 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SKP2 Sensitizes Bromocriptine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Prolactinoma Cells.Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Apr;49(2):358-373. doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.017. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 27488872 Free PMC article.
-
A gene signature consisting of ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes of SKP2 is associated with clinical outcome in breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 15;12(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06451-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35169199 Free PMC article.
-
Paeoniflorin exerts antitumor effects by inactivating S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in glioma cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1052-1062. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6175. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29286139 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Skp2 inhibits the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):181-92. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0527-8. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23229098
References
-
- Bonofiglio D., Gabriele S., Aquila S., Catalano S., Gentile M., Middea E., Giordano F., Ando S. (2005). Estrogen receptor alpha binds to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor response element and negatively interferes with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma signaling in breast cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 6139–614710.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2453 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

