In utero activation of fetal memory T cells alters host regulatory gene expression and affects HIV susceptibility
- PMID: 22280894
- PMCID: PMC3725764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.01.003
In utero activation of fetal memory T cells alters host regulatory gene expression and affects HIV susceptibility
Abstract
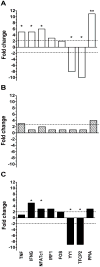
In utero priming to malaria antigens renders cord blood mononuclear cells (CBMC) more susceptible to productive HIV infection in vitro in the absence of exogenous stimulation. This provides a unique model to better understand mechanisms affecting lymphocyte susceptibility to HIV infection in vivo. Effector memory CD3(+)CD4(+) T cells (T(EM)) were the exclusive initial targets of HIV with rapid spread to central memory cells. HIV susceptibility correlated with increased expression of CD25 and HLA-DR on T(EM). Virus entered all samples equally, however gag/pol RNA was only detected in HIV susceptible samples, suggesting regulation of proviral gene transcription. Targeted analysis of human genes in memory T cells showed greater expression of IFNG, NFATc1, IRF1, FOS, and PPIA and decreased expression YY1 and TFCP2 in HIV susceptible samples. Thus fetal priming to exogenous antigens enhances specific proviral gene transcription pathways in effector memory cells that may increase risk of vertical transmission of HIV.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



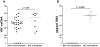
References
-
- Ahmad N, Mehta R, Harris DT. HIV-1 replication and gene expression occur at higher levels in neonatal blood naive and memory T-lymphocytes compared with adult blood cells. Virology. 2011;413(1):39–46. - PubMed
-
- Battistini A, Marsili G, Sgarbanti M, Ensoli B, Hiscott J. IRF regulation of HIV-1 long terminal repeat activity. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research: The Official Journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research. 2002;22(1):27–37. - PubMed
-
- Brahmbhatt H, Kigozi G, Wabwire-Mangen F, Serwadda D, Sewankambo N, Lutalo T, Wawer MJ, Abramowsky C, Sullivan D, Gray R. The effects of placental malaria on mother-to-child HIV transmission in Rakai, Uganda. AIDS. 2003;17(17):2539–2541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

