Bhlhb5 and Prdm8 form a repressor complex involved in neuronal circuit assembly
- PMID: 22284184
- PMCID: PMC3269007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.035
Bhlhb5 and Prdm8 form a repressor complex involved in neuronal circuit assembly
Abstract
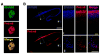
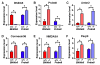
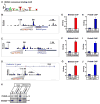
Although transcription factors that repress gene expression play critical roles in nervous system development, their mechanism of action remains to be understood. Here, we report that the Olig-related transcription factor Bhlhb5 (also known as Bhlhe22) forms a repressor complex with the PR/SET domain protein, Prdm8. We find that Bhlhb5 binds to sequence-specific DNA elements and then recruits Prdm8, which mediates the repression of target genes. This interaction is critical for repressor function since mice lacking either Bhlhb5 or Prdm8 have strikingly similar cellular and behavioral phenotypes, including axonal mistargeting by neurons of the dorsal telencephalon and abnormal itch-like behavior. We provide evidence that Cadherin-11 functions as target of the Prdm8/Bhlhb5 repressor complex that must be repressed for proper neural circuit formation to occur. These findings suggest that Prdm8 is an obligate partner of Bhlhb5, forming a repressor complex that directs neural circuit assembly in part through the precise regulation of Cadherin-11.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
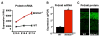

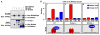
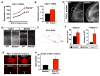
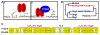
References
-
- Ancelin K, Lange UC, Hajkova P, Schneider R, Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T, Surani MA. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:623–630. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand N, Castro DS, Guillemot F. Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:517–530. - PubMed
-
- Bramblett DE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Tsai MJ. BHLHB4 is a bHLH transcriptional regulator in pancreas and brain that marks the dimesencephalic boundary. Genomics. 2002;79:402–412. - PubMed
-
- Bramblett DE, Pennesi ME, Wu SM, Tsai MJ. The transcription factor Bhlhb4 is required for rod bipolar cell maturation. Neuron. 2004;43:779–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

