Changes in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced by the Morris water maze task
- PMID: 22286233
- PMCID: PMC3887700
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-012-2254-9
Changes in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced by the Morris water maze task
Abstract
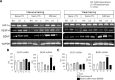
The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effects on hippocampal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in rats when they experience hippocampal-dependent spatial learning via the Morris water maze (MWM) task. Rats underwent one of two different versions of the MWM: weak or intensive. After one day of intensive training, a highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure VEGF protein levels in the hippocampus, cortex, and serum, and higher levels were found in the trained group compared to a naive control group. VEGF levels also increased in rats that swam only for durations equal to the intensive training periods. In contrast, rats trained under the weaker MWM paradigm for five days showed a decrease in hippocampal VEGF protein level. Mimicking increases in neuronal VEGF in the hippocampus by direct infusion of VEGF into CA1 resulted in up-regulation of the phosphorylation of the cAMP response element-binding (CREB) protein and the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II (CaMKII). These results suggest that VEGF may be a physiological parameter involved in learning procedures that include physical activity.
Figures



References
-
- Bach M.E., Hawkins R.D., Osman M., Kandel E.R., Mayford M. Impairment of spatial but not contextual memory in CaMKII mutant mice with a selective loss of hippocampal LTP in the range of the theta frequency. Cell. 1995;81:905–915. - PubMed
-
- Beversdorf D.Q., Hughes J.D., Steinberg B.A., Lewis L.D., Heilman K.M. Noradrenergic modulation of cognitive flexibility in problem solving. Neuroreport. 1999;10:2763–2767. - PubMed
-
- Cao L., Jiao X., Zuzga D.S., Liu Y., Fong D.M., Young D., During M.J. VEGF links hippocampal activity with neurogenesis, learning and memory. Nat. Genet. 2004;36:827–835. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Pinilla F., Dao L., So V. Physical exercise induces FGF-2 and its mRNA in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1997;764:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson T., Puntschart A., Kaijser L., Jansson E., Sundberg C.J. Exercise-induced expression of angiogenesis-related transcription and growth factors in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;276:H679–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

