A recessive mutation resulting in a disabling amino acid substitution (T194R) in the LHX3 homeodomain causes combined pituitary hormone deficiency
- PMID: 22286346
- PMCID: PMC3355643
- DOI: 10.1159/000335929
A recessive mutation resulting in a disabling amino acid substitution (T194R) in the LHX3 homeodomain causes combined pituitary hormone deficiency
Abstract
Background/aims: Recessive mutations in the LHX3 homeodomain transcription factor gene are associated with developmental disorders affecting the pituitary and nervous system. We describe pediatric patients with combined pituitary hormone deficiency (CPHD) who harbor a novel mutation in LHX3.
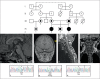
Methods: Two female siblings from related parents were examined. Both patients had neonatal complications. The index patient had CPHD featuring deficiencies of GH, LH, FSH, PRL, and TSH, with later onset of ACTH deficiency. She also had a hypoplastic anterior pituitary, respiratory distress, hearing impairment, and limited neck rotation. The LHX3 gene was sequenced and the biochemical properties of the predicted altered proteins were characterized.
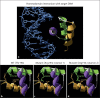
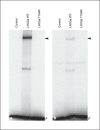
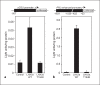
Results: A novel homozygous mutation predicted to change amino acid 194 from threonine to arginine (T194R) was detected in both patients. This amino acid is conserved in the DNA-binding homeodomain. Computer modeling predicted that the T194R change would alter the homeodomain structure. The T194R protein did not bind tested LHX3 DNA recognition sites and did not activate the α-glycoprotein and PRL target genes.
Conclusion: The T194R mutation affects a critical residue in the LHX3 protein. This study extends our understanding of the phenotypic features, molecular mechanism, and developmental course associated with mutations in the LHX3 gene.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

References
-
- Kelberman D, Dattani MT. Role of transcription factors in midline central nervous system and pituitary defects. Endocr Dev. 2009;14:67–82. - PubMed
-
- Pfäffle R, Klammt J. Pituitary transcription factors in the aetiology of combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;25:43–60. - PubMed
-
- Prince KL, Walvoord EC, Rhodes SJ. The role of homeodomain transcription factors in heritable pituitary disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:727–737. - PubMed

