How to recognize late-onset hypogonadism in men with sexual dysfunction
- PMID: 22286862
- PMCID: PMC3735094
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2011.138
How to recognize late-onset hypogonadism in men with sexual dysfunction
Abstract
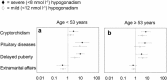
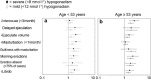
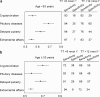
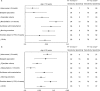
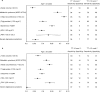
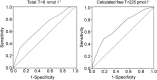
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH) has been considered the most common form of male hypogonadism with a prevalence of approximately 1 in 100 men. Diagnosis of LOH should be made in symptomatic men with unequivocally low serum testosterone (T) levels. However, its clinical presentation is often insidious and difficult to recognize because it is characterized by nonspecific symptoms that make differential diagnosis with physiological ageing problematic. Sexual dysfunction is the most important determinant for medical consultation and the most specific symptom associated with low T. We therefore analysed a consecutive series of 1734 subjects who attended our unit for sexual dysfunction to investigate the associations between low T (different thresholds), sexual parameters, medical history data (delayed puberty, pituitary disease or cryptorchidism) and their physical exam results. Metabolic parameters, in particular waist circumference, display the greatest accuracy in detecting low T. We found that only the association of several symptoms and signs could significantly raise the clinical suspicion of low T. Structured inventories, which cluster together symptoms and signs of hypogonadism, can help clinicians suspect androgen deficiency. In particular, structured interviews, such as ANDROTEST, have been demonstrated to have a greater accuracy when compared to self reported questionnaires in detecting low T levels.
Figures


References
-
- Tajar A, Forti G, O'Neill TW, Lee DM, Silman AJ, et al. Characteristics of secondary, primary, and compensated hypogonadism in aging men: evidence from the European Male Ageing Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:1810–8. - PubMed
-
- Buvat J, Maggi M, Gooren L, Guay AT, Kaufman J, et al. Endocrine aspects of male sexual dysfunctions. In: Montorsi F, Basson R, Adaikan G, Becher E, Clayton A, Giuliano G, Khoury S, Sharlip I, editors. Sexual Medicine, Sexual Dysfunctions in Men and Women. Proceedings of the 3rd International Consultation on Sexual Medicine Paris; Health Publication Ltd; 2010. p681. - PubMed
-
- Morelli A, Corona G, Filippi S, Ambrosini S, Forti G, et al. Which patients with sexual dysfunction are suitable for testosterone replacement therapy. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007;30:880–8. - PubMed
-
- Corona G, Rastrelli G, Forti G, Maggi M. Update in testosterone therapy for men. J Sex Med. 2011;8:639–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

