Influence of cations on growth of thermophilic Geobacillus spp. and Anoxybacillus flavithermus in planktonic culture
- PMID: 22287005
- PMCID: PMC3302610
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.06951-11
Influence of cations on growth of thermophilic Geobacillus spp. and Anoxybacillus flavithermus in planktonic culture
Abstract
Free ions of Na(+), K(+), Ca(2+), and Mg(2+) influenced the optical density of planktonic cultures of thermophilic bacilli. Anoxybacillus flavithermus E16 and Geobacillus sp. strain F75 (milk powder manufacturing plant isolates) and A. flavithermus DSM 2641 and G. thermoleovorans DSM 5366 were studied. Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) were associated with increases in optical density more so than Na(+) and K(+). Overall, it appeared that Ca(2+) and/or Mg(2+) was required for the production of protein in thermophilic bacilli, as shown by results obtained with A. flavithermus E16, which was selected for further study.
Figures
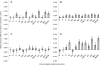
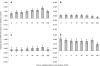
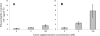
References
-
- Anema SG. 2009. Effect of milk solids concentration on the pH, soluble calcium and soluble phosphate levels of milk during heating. Dairy Sci. Technol. 89:501–510
-
- BD Biosciences 2006. Advanced bioprocessing. BD Bionutrients technical manual, 3rd ed. BD Biosciences, Sparks, MD
-
- Burgess SA, Lindsay D, Flint SH. 2010. Thermophilic bacilli and their importance in dairy processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 144:215–225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

