IGFBP ratio confers resistance to IGF targeting and correlates with increased invasion and poor outcome in breast tumors
- PMID: 22287600
- PMCID: PMC3306532
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1806
IGFBP ratio confers resistance to IGF targeting and correlates with increased invasion and poor outcome in breast tumors
Abstract
Purpose: To improve the significance of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) as a prognostic and potentially predictive marker in patients with breast cancer.
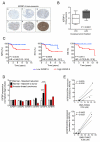
Experimental design: Increased IGFBP-5 expression was identified in MCF-7 cells resistant (MCF-7R4) to the IGF-1R/insulin receptor (InsR) inhibitor BMS-536924 and its role examined by targeted knockdown and overexpression in multiple experimental models. Protein expression of IGFBP-5 was measured by immunohistochemistry in a cohort of 76 patients with breast cancer to examine correlative associations with invasive tumor fraction and outcome. The use of a combined IGFBP-5/IGFBP-4 (BPR) expression ratio was applied to predict anti-IGF-1R/InsR response in a panel of breast cancer lines and outcome in multiple breast tumor cohorts.
Results: IGFBP-5 knockdown decreased BMS-536924 resistance in MCF-7R4 cells, whereas IGFBP-5 overexpression in MCF-7 cells conferred resistance. When compared with pathologically normal reduction mammoplasty tissue, IGFBP-5 expression levels were upregulated in both invasive and histologically normal adjacent breast cancer tissue. In both univariate and multivariate modeling, metastasis-free survival, recurrence free survival (RFS), and overall survival (OS) were significantly associated with high IGFBP-5 expression. Prognostic power of IGFBP-5 was further increased with the addition of IGFBP-4 where tumors were ranked based upon IGFBP-5/IGFBP-4 expression ratio (BPR). Multiple breast cancer cohorts confirm that BPR (high vs. low) was a strong predictor of RFS and OS.
Conclusion: IGFBP-5 expression is a marker of poor outcome in patients with breast cancer. An IGFBP-5/IGFBP-4 expression ratio may serve as a surrogate biomarker of IGF pathway activation and predict sensitivity to anti-IGF-1R targeting.
Figures


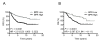
References
-
- Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L, Yuan J, Havre PA, Gumbs AA, et al. Insulin- like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res. 1997 Aug 1;57(15):3079–83. - PubMed
-
- McGuire WL, Jr., Jackson JG, Figueroa JA, Shimasaki S, Powell DR, Yee D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) expression by breast cancer cells: use of IGFBP-1 as an inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor action. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Sep 2;84(17):1336–41. - PubMed
-
- Paik S. Expression of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA in breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22(1):31–8. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Zi X, Zhao Y, Mascarenhas D, Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin) J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001 Dec 19;93(24):1852–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

