Immunology in clinic review series; focus on autoinflammatory diseases: update on monogenic autoinflammatory diseases: the role of interleukin (IL)-1 and an emerging role for cytokines beyond IL-1
- PMID: 22288582
- PMCID: PMC3374271
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04533.x
Immunology in clinic review series; focus on autoinflammatory diseases: update on monogenic autoinflammatory diseases: the role of interleukin (IL)-1 and an emerging role for cytokines beyond IL-1
Abstract
OTHER THEMES PUBLISHED IN THIS IMMUNOLOGY IN THE CLINIC REVIEW SERIES Allergy, Host Responses, Cancer, Type 1 diabetes and viruses, Metabolic diseases.
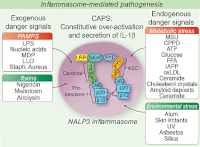
Summary: The disease-based discovery of the molecular basis for autoinflammatory diseases has led not only to a rapidly growing number of clinically and genetically identifiable disorders, but has unmantled key inflammatory pathways such as the potent role of the alarm cytokine interleukin (IL)-1 in human disease. Following its initial failures in the treatment of sepsis and the moderate success in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, IL-1 blocking therapies had a renaissance in the treatment of a number of autoinflammatory conditions, and IL-1 blocking therapies have been Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for the treatment of the autoinflammatory conditions: cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS). CAPS and deficiency of the IL-1 receptor antagonist (DIRA), both genetic conditions with molecular defects in the IL-1 pathway, have provided a pathogenic rationale to IL-1 blocking therapies, and the impressive clinical results confirmed the pivotal role of IL-1 in human disease. Furthermore, IL-1 blocking strategies have shown clinical benefit in a number of other genetically defined autoinflammatory conditions, and diseases with clinical similarities to the monogenic disorders and not yet identified genetic causes. The discovery that IL-1 is not only triggered by infectious danger signals but also by danger signals released from metabolically 'stressed' or even dying cells has extended the concept of autoinflammation to disorders such as gout, and those that were previously not considered inflammatory, such as type 2 diabetes, coronary artery disease, obesity and some degenerative diseases, and provided the conceptual framework to target IL-1 in these diseases. Despite the tremendous success of IL-1 blocking therapy, the use of these agents in a wider spectrum of autoinflammatory conditions has uncovered disease subsets that are not responsive to IL-1 blockade, including the recently discovered proteasome-associated autoinflammatory syndromes such as chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatitis with lipodystrophy and elevated temperatures (CANDLE), Japanese autoinflammatory syndrome with lipodystrophy (JASL), Nakajo-Nishimura syndrome (NNS) and joint contractures, muscle atrophy, panniculitis induced lipodystrophy (JMP), and urge the continued quest to characterize additional dysregulated innate immune pathways that cause autoinflammatory conditions.
Published 2011. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures

References
-
- International FMF Consortium. Ancient missense mutations in a new member of the RoRet gene family are likely to cause familial Mediterranean fever. Cell. 1997;90:797–807. - PubMed
-
- French FMF Consortium. A candidate gene for familial Mediterranean fever. Nat Genet. 1997;17:25–31. - PubMed
-
- McDermott MF, Aksentijevich I, Galon J, et al. Germline mutations in the extracellular domains of the 55 kDa TNF receptor, TNFR1, define a family of dominantly inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Cell. 1999;97:133–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

