Biological activity of anti-CD20 multivalent HPMA copolymer-Fab' conjugates
- PMID: 22288884
- PMCID: PMC3299848
- DOI: 10.1021/bm201656k
Biological activity of anti-CD20 multivalent HPMA copolymer-Fab' conjugates
Abstract
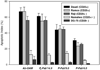
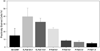
High-molecular-weight, branched N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymers were synthesized and conjugated with Fab' fragments of the anti-CD20 antibody, 1F5. This produced multivalent conjugates with varying valency (amount of Fab' per macromolecule) targeted to the B-cell antigen CD20. The apoptotic activity of the conjugates was screened against several B-cell lymphomas with varied expression levels of CD20 (Raji, Daudi, Ramos, Namalwa, and DG-75). The multivalent conjugates had the strongest activity against cells that had the highest expression of CD20 and failed to demonstrate any measurable activity against lymphomas that did not express the antigen. Furthermore, there was an apparent dose-dependent response to treatment with multivalent conjugates. At optimal valence and concentration, the apoptotic activity of HPMA copolymer-Fab' conjugates superseded that of free anti-CD20 Ab that was hyper-cross-linked with a polyclonal, secondary Ab.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

