Gene silencing of IL-12 in dendritic cells inhibits autoimmune arthritis
- PMID: 22289162
- PMCID: PMC3293054
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-19
Gene silencing of IL-12 in dendritic cells inhibits autoimmune arthritis
Abstract
Background: We have previously demonstrated that immune modulation can be accomplished by administration of gene silenced dendritic cells (DC) using siRNA. In this study, we demonstrate the therapeutic utilization of shRNA-modified DC as an antigen-specific tolerogenic vaccine strategy for autoimmune arthritis.
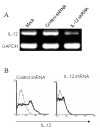
Methods: A shRNA that specifically targets IL-12 p35 was designed and cloned into a plasmid vectors (IL-12 shRNA). Bone marrow-derived DC from DBA/1 mice were transfected with the IL-12 shRNA construct in vitro. Mice with collagen II (CII)-induced arthritis (CIA) were treated with the modified DCs expressing the shRNA. Recall response and disease progression were assessed.
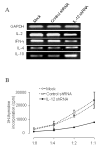
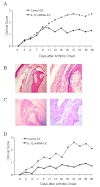
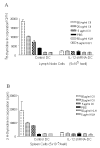
Results: After gene silencing of IL-12 in DC, DC were shown to selectively inhibit T cell proliferation on recall responses and in an MLR. In murine CIA, we demonstrated that administration of IL-12 shRNA-expressing DC that were pulsed with CII inhibited progression of arthritis. The therapeutic effects were evidenced by decreased clinical scores, inhibition of inflammatory cell infiltration in the joint, and suppression of T cell and B cell responses to CII.
Conclusion: We demonstrate a novel tolerance-inducing protocol for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory joint disease in which the target antigen is known, utilizing DNA-directed RNA interference.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antigen-induced, tolerogenic CD11c+,CD11b+ dendritic cells are abundant in Peyer's patches during the induction of oral tolerance to type II collagen and suppress experimental collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):887-98. doi: 10.1002/art.21647. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508971
-
Preventing autoimmune arthritis using antigen-specific immature dendritic cells: a novel tolerogenic vaccine.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(5):R141. doi: 10.1186/ar2031. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16911769 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of established murine collagen-induced arthritis by a single inoculation of short-term lipopolysaccharide-stimulated dendritic cells.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Sep;67(9):1235-41. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.072199. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18056756
-
Dendritic cells transfected with DNA constructs encoding CCR9, IL-10, and type II collagen demonstrate induction of immunological tolerance in an arthritis model.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1447897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447897. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39161770 Free PMC article.
-
Type II collagen oral tolerance; mechanism and role in collagen-induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(6):581-9. doi: 10.1007/s10165-009-0210-0. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Mod Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19697097 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic suppression of autoimmune arthritis through concurrent treatment with tolerogenic DC and MSC.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 23;7:43188. doi: 10.1038/srep43188. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28230210 Free PMC article.
-
DC-Based Immunotherapy Combined with Low-Dose Methotrexate Effective in the Treatment of Advanced CIA in Mice.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:834085. doi: 10.1155/2015/834085. Epub 2015 Jun 28. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26221616 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic Cell-Mediated Th2 Immunity and Immune Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 1;20(9):2159. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092159. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD38 Deficiency Downregulates the Onset and Pathogenesis of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through the NF-κB Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2019 Mar 5;2019:7026067. doi: 10.1155/2019/7026067. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 30949517 Free PMC article.
-
Lower level of IL‑35 and its reduced inhibition in Th17 cells in patients with bone marrow mononuclear cells Coombs test‑positive hemocytopenia.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):2973-2981. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8252. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abeles AM, Pillinger MH. The role of the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: cartilage destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull NYU Hospital Joint Diseases. 2006;64:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Smeets TJ, Barg EC, Kraan MC, Smith MD, Breedveld FC, Tak PP. Analysis of the cell infiltrate and expression of proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in arthroscopic synovial biopsies: comparison with synovial samples from patients with end stage, destructive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:635–638. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.7.635. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, Galjaard S, Youssef PP, Smith MD, Tak PP. Analysis of the cell infiltrate and expression of matrix metalloproteinases and granzyme B in paired synovial biopsy specimens from the cartilage-pannus junction in patients with RA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60:561–565. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.6.561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M. The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:S4–S11. - PubMed
-
- Yamada H, Nakashima Y, Okazaki K, Mawatari T, Fukushi JI, Kaibara N, Hori A, Iwamoto Y, Yoshikai Y. Th1 but not Th17 cells predominate in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1299–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

