Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells
- PMID: 22289780
- PMCID: PMC3307887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.01.002
Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells
Abstract
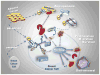
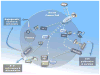
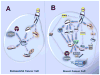
Significant correlations between obesity and incidence of various cancers have been reported. Obesity, considered a mild inflammatory process, is characterized by a high level of secretion of several cytokines from adipose tissue. These molecules have disparate effects, which could be relevant to cancer development. Among the inflammatory molecules, leptin, mainly produced by adipose tissue and overexpressed with its receptor (Ob-R) in cancer cells is the most studied adipokine. Mutations of leptin or Ob-R genes associated with obesity or cancer are rarely found. However, leptin is an anti-apoptotic molecule in many cell types, and its central roles in obesity-related cancers are based on its pro-angiogenic, pro-inflammatory and mitogenic actions. Notably, these leptin actions are commonly reinforced through entangled crosstalk with multiple oncogenes, cytokines and growth factors. Leptin-induced signals comprise several pathways commonly triggered by many cytokines (i.e., canonical: JAK2/STAT; MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI-3K/AKT1 and, non-canonical signaling pathways: PKC, JNK and p38 MAP kinase). Each of these leptin-induced signals is essential to its biological effects on food intake, energy balance, adiposity, immune and endocrine systems, as well as oncogenesis. This review is mainly focused on the current knowledge of the oncogenic role of leptin in breast cancer. Additionally, leptin pro-angiogenic molecular mechanisms and its potential role in breast cancer stem cells will be reviewed. Strict biunivocal binding-affinity and activation of leptin/Ob-R complex makes it a unique molecular target for prevention and treatment of breast cancer, particularly in obesity contexts.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
References
-
- WHO. World Health Organization Fact Sheet for World Wide Prevalence of Obesity. 2006 http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html.
-
- Baskin ML, Ard J, Franklin F, Allison DB. Prevalence of obesity in the United States. Obes Rev. 2005;6:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Ogden CL, Carroll MD. Prevalence and trends in overweight in Mexican-american adults and children. Nutr Rev. 2004;62:S144–148. - PubMed
-
- Haslam DW, James WP. Obesity. Lancet. 2005;366:1197–1209. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight, obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–1555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous