Characterization of a novel inactivated Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis vaccine candidate generated using a modified cI857/λ PR/gene E expression system
- PMID: 22290147
- PMCID: PMC3318409
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.06264-11
Characterization of a novel inactivated Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis vaccine candidate generated using a modified cI857/λ PR/gene E expression system
Abstract
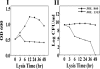
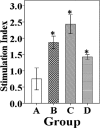
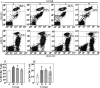
A new strategy to develop an effective vaccine is essential to control food-borne Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis infections. Bacterial ghosts (BGs), which are nonliving, Gram-negative bacterial cell envelopes, are generated by expulsion of the cytoplasmic contents from bacterial cells through controlled expression using the modified cI857/λ P(R)/gene E expression system. In the present study, the pJHL99 lysis plasmid carrying the mutated lambda pR37-cI857 repressor and PhiX174 lysis gene E was constructed and transformed in S. Enteritidis to produce a BG. Temperature induction of the lysis gene cassette at 42°C revealed quantitative killing of S. Enteritidis. The S. Enteritidis ghost was characterized using scanning and transmission electron microscopy to visualize the transmembrane tunnel structure and loss of cytoplasmic materials, respectively. The efficacy of the BG as a vaccine candidate was evaluated in a chicken model using 60 10-day-old chickens, which were divided into four groups (n = 15), A, B, C, and D. Group A was designated as the nonimmunized control group, whereas the birds in groups B, C, and D were immunized via the intramuscular, subcutaneous, and oral routes, respectively. The chickens from all immunized groups showed significant increases in plasma IgG and intestinal secretory IgA levels. The lymphocyte proliferation response and CD3(+) CD4(+) and CD3(+) CD8(+) T cell subpopulations were also significantly increased in all immunized groups. The data indicate that both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses are robustly stimulated. Based on an examination of the protection efficacy measured by observations of gross lesions in the organs and bacterial recovery, the candidate vaccine can provide efficient protection against virulent challenge.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of a biosafety enhanced and immunogenic Salmonella enteritidis ghost using an antibiotic resistance gene free plasmid carrying a bacteriophage lysis system.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):e78193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078193. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205152 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis ghosts carrying the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit are capable of inducing enhanced protective immune responses.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014 Jun;21(6):799-807. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00016-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24671556 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of adaptive immune responses induced by a new genetically inactivated Salmonella Enteritidis vaccine.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 May;37(3):159-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 May 17. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24878070
-
Age of challenge is important in Salmonella Enteritidis studies in pullets and hens: a systematic review.Avian Pathol. 2025 Apr;54(2):159-167. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2024.2410873. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Avian Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39392015
-
Progress in the application of Salmonella vaccines in poultry: A mini review.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2024 Dec;278:110855. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2024.110855. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2024. PMID: 39561520 Review.
Cited by
-
Surface engineered polyanhydride-based oral Salmonella subunit nanovaccine for poultry.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Nov 30;13:8195-8215. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S185588. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30555234 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a biosafety enhanced and immunogenic Salmonella enteritidis ghost using an antibiotic resistance gene free plasmid carrying a bacteriophage lysis system.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 18;8(10):e78193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078193. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205152 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage-encoded protein utilization in bacterial ghost production: a mini-review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 29;40(9):284. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04091-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39073496 Review.
-
Highly feasible immunoprotective multicistronic SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate blending novel eukaryotic expression and Salmonella bactofection.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 22;36:211-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.07.007. eCollection 2022 Feb. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35116175 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrochloric acid-treated Bacillus subtilis ghosts induce IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha in murine macrophage.Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022;18(2):267-276. doi: 10.1007/s13273-022-00221-5. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35069752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrow PA. 2007. Salmonella infections: immune and non-immune protection with vaccines. Avian Pathol. 36:1–13 - PubMed
-
- Berthelot-Hérault F, Mompart F, Zygmunt MS, Dubray G, Duchet-Suchaux M. 2003. Antibody responses in the serum and gut of chicken lines differing in cecal carriage of Salmonella Enteritidis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 96:43–52 - PubMed
-
- Casadevall A. 1998. Antibody-mediated protection against intracellular pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 6:102–107 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

