Outcomes of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in the United States
- PMID: 22290268
- PMCID: PMC3299822
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318245b2af
Outcomes of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in the United States
Abstract
Background: ABO incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation is an important modality to facilitate living donor transplant for incompatible pairs. To date, reports of the outcomes from this practice in the United States have been limited to single-center studies.
Methods: Using the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients, we identified 738 patients who underwent live-donor ABOi kidney transplantation between January 1, 1995, and March 31, 2010. These were compared with matched controls that underwent ABO compatible live-donor kidney transplantation. Subgroup analyses among ABOi recipients were performed according to donor blood type, recipient blood type, and transplant center ABOi volume.
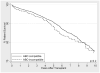
Results: When compared with ABO compatible-matched controls, long-term patient survival of ABOi recipients was not significantly different between the cohorts (P=0.2). However, graft loss was significantly higher, particularly in the first 14 days posttransplant (subhazard ratio, 2.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.43-3.84; P=0.001), with little to no difference beyond day 14 (subhazard ratio, 1.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.99-1.54; P=0.058). In subgroup analyses among ABOi recipients, no differences in survival were seen by donor blood type, recipient blood type, or transplant center ABOi volume.
Conclusions: These results support the use and dissemination of ABOi transplantation when a compatible live donor is not available, but caution that the highest period of risk is immediately posttransplant.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Gentry SE, Montgomery RA, Segev DL. Kidney Paired Donation: Fundamentals, Limitations, and Expansions. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57(1):144–151. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery RA. Renal transplantation across HLA and ABO antibody barriers: integrating paired donation into desensitization protocols. Am J Transplant. 2010;10(3):449–457. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery RA, Simpkins CE, Segev DL. New options for patients with donor incompatibilities. Transplantation. 2006;82(2):164–165. - PubMed
-
- Gentry S, Montgomery R, Segev D. Blood group O recipients and compatible kidney paired donation. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:392–392.
-
- Segev DL, Kucirka LM, Gentry SE, Montgomery RA. Utilization and outcomes of kidney paired donation in the United States. Transplantation. 2008;86(4):502–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

