YY1 controls immunoglobulin class switch recombination and nuclear activation-induced deaminase levels
- PMID: 22290437
- PMCID: PMC3318595
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.05989-11
YY1 controls immunoglobulin class switch recombination and nuclear activation-induced deaminase levels
Abstract
Activation-induced deaminase (AID) is an enzyme required for class switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM), processes that ensure antibody maturation and expression of different immunoglobulin isotypes. AID function is tightly regulated by tissue- and stage-specific expression, nuclear localization, and protein stability. Transcription factor YY1 is crucial for early B cell development, but its function at late B cell stages is unknown. Here, we show that YY1 conditional knockout in activated splenic B cells interferes with CSR. Knockout of YY1 did not affect B cell proliferation, transcription of the AID and IgM genes, or levels of various switch region germ line transcripts. However, we show that YY1 physically interacts with AID and controls the accumulation of nuclear AID, at least in part, by increasing nuclear AID stability. We show for the first time that YY1 plays a novel role in CSR and controls nuclear AID protein levels.
Figures

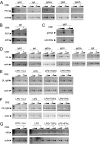
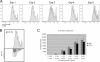
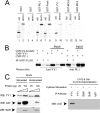
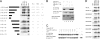

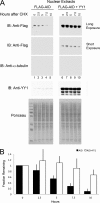
References
-
- Ballantyne J, Henry DL, Marcu KB. 1997. Antibody class switch recombinase activity is B cell stage specific and functions stochastically in the absence of ‘targeted accessibility’ control. Int. Immunol. 9:963–974 - PubMed
-
- Brar SS, Watson M, Diaz M. 2004. Activation-induced cytosine deaminase (AID) is actively exported out of the nucleus but retained by the induction of DNA breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 279:26395–26401 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
