A bacterial siren song: intimate interactions between Neisseria and neutrophils
- PMID: 22290508
- PMCID: PMC3569855
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2713
A bacterial siren song: intimate interactions between Neisseria and neutrophils
Abstract
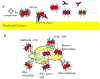
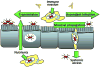
Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis are Gram-negative bacterial pathogens that are exquisitely adapted for growth at human mucosal surfaces and for efficient transmission between hosts. One factor that is essential to neisserial pathogenesis is the interaction between the bacteria and neutrophils, which are recruited in high numbers during infection. Although this vigorous host response could simply reflect effective immune recognition of the bacteria, there is mounting evidence that in fact these obligate human pathogens manipulate the innate immune response to promote infectious processes. This Review summarizes the mechanisms used by pathogenic neisseriae to resist and modulate the antimicrobial activities of neutrophils. It also details some of the major outstanding questions about the Neisseria-neutrophil relationship and proposes potential benefits of this relationship for the pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schielke S, Frosch M, Kurzai O. Virulence determinants involved in differential host niche adaptation of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010;199:185–96. - PubMed
-
- Marri PR, et al. Genome sequencing reveals widespread virulence gene exchange among human Neisseria species. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11835. In this investigation, the authors sequence the genomes of multiple commensal and pathogenic neisseriae to show that supposed ‘virulence’ genes are present in many commensal species. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wiesner PJ, Thompson SE., 3rd Gonococcal diseases. Dis Mon. 1980;26:1–44. - PubMed
-
- Burg ND, Pillinger MH. The neutrophil: function and regulation in innate and humoral immunity. Clin Immunol. 2001;99:7–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

