A 5'-terminal phosphate is required for stable ternary complex formation and translation of leaderless mRNA in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 22291205
- PMCID: PMC3285938
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.027698.111
A 5'-terminal phosphate is required for stable ternary complex formation and translation of leaderless mRNA in Escherichia coli
Abstract
The bacteriophage λ's cI mRNA was utilized to examine the importance of the 5'-terminal phosphate on expression of leadered and leaderless mRNA in Escherichia coli. A hammerhead ribozyme was used to produce leadered and leaderless mRNAs, in vivo and in vitro, that contain a 5'-hydroxyl. Although these mRNAs may not occur naturally in the bacterial cell, they allow for the study of the importance of the 5'-phosphorylation state in ribosome binding and translation of leadered and leaderless mRNAs. Analyses with mRNAs containing either a 5'-phosphate or a 5'-hydroxyl indicate that leaderless cI mRNA requires a 5'-phosphate for stable ribosome binding in vitro as well as expression in vivo. Ribosome-binding assays show that 30S subunits and 70S ribosomes do not bind as strongly to 5'-hydroxyl as they do to 5'-phosphate containing leaderless mRNA and the tRNA-dependent ternary complex is less stable. Additionally, filter-binding assays revealed that the 70S ternary complex formed with a leaderless mRNA containing a 5'-hydroxyl has a dissociation rate (k(off)) that is 4.5-fold higher compared with the complex formed with a 5'-phosphate leaderless mRNA. Fusion to a lacZ reporter gene revealed that leaderless cI mRNA expression with a 5'-hydroxyl was >100-fold lower than the equivalent mRNA with a 5'-phosphate. These data indicate that a 5'-phosphate is an important feature of leaderless mRNA for stable ribosome binding and expression.
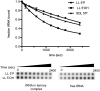
Figures

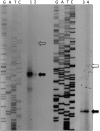
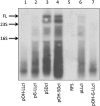
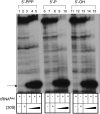
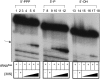


References
-
- Chang B, Halgamuge S, Tang S 2006. Analysis of SD sequences in completed microbial genomes: Non-SD-led genes are as common as SD-led genes. Gene 373: 90–99 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
