Interferon-alpha administration enhances CD8+ T cell activation in HIV infection
- PMID: 22291932
- PMCID: PMC3265460
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030306
Interferon-alpha administration enhances CD8+ T cell activation in HIV infection
Abstract
Background: Type I interferons play important roles in innate immune defense. In HIV infection, type I interferons may delay disease progression by inhibiting viral replication while at the same time accelerating disease progression by contributing to chronic immune activation.
Methods: To investigate the effects of type I interferons in HIV-infection, we obtained cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples from 10 subjects who participated in AIDS Clinical Trials Group Study 5192, a trial investigating the activity of systemic administration of IFNα for twelve weeks to patients with untreated HIV infection. Using flow cytometry, we examined changes in cell cycle status and expression of activation antigens by circulating T cells and their maturation subsets before, during and after IFNα treatment.
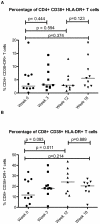
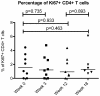
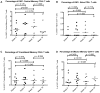
Results: The proportion of CD38+HLA-DR+CD8+ T cells increased from a mean of 11.7% at baseline to 24.1% after twelve weeks of interferon treatment (p = 0.006). These frequencies dropped to an average of 20.1% six weeks after the end of treatment. In contrast to CD8+ T cells, the frequencies of activated CD4+ T cells did not change with administration of type I interferon (mean percentage of CD38+DR+ cells = 2.62% at baseline and 2.17% after 12 weeks of interferon therapy). As plasma HIV levels fell with interferon therapy, this was correlated with a "paradoxical" increase in CD8+ T cell activation (p<0.001).
Conclusion: Administration of type I interferon increased expression of the activation markers CD38 and HLA DR on CD8+ T cells but not on CD4+ T cells of HIV+ persons. These observations suggest that type I interferons may contribute to the high levels of CD8+ T cell activation that occur during HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Leng Q, Borkow G, Weisman Z, Stein M, Kalinkovich A, et al. Immune activation correlates better than HIV plasma viral load with CD4 T-cell decline during HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001;27(4):389–397. - PubMed
-
- Muro-Cacho CA, Pantaleo G, Fauci AS. Analysis of apoptosis in lymph nodes of HIV-infected persons. Intensity of apoptosis correlates with the general state of activation of the lymphoid tissue and not with stage of disease or viral burden. J Immunol. 1995;154(10):5555–5566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1U01-AI069484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01-AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01-AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 36219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01-AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI065361/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL108743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

