Mechanistic basis for high reactivity of (salen)Co-OTs in the hydrolytic kinetic resolution of terminal epoxides
- PMID: 22292515
- PMCID: PMC3292627
- DOI: 10.1021/jo300181f
Mechanistic basis for high reactivity of (salen)Co-OTs in the hydrolytic kinetic resolution of terminal epoxides
Abstract
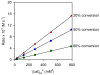
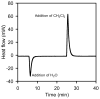
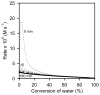
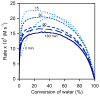
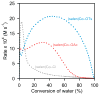
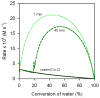
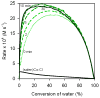
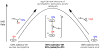
The (salen)Co(III)-catalyzed hydrolytic kinetic resolution (HKR) of terminal epoxides is a bimetallic process with a rate controlled by partitioning between a nucleophilic (salen)Co-OH catalyst and a Lewis acidic (salen)Co-X catalyst. The commonly used (salen)Co-OAc and (salen)Co-Cl precatalysts undergo complete and irreversible counterion addition to epoxide during the course of the epoxide hydrolysis reaction, resulting in quantitative formation of weakly Lewis acidic (salen)Co-OH and severely diminished reaction rates in the late stages of HKR reactions. In contrast, (salen)Co-OTs maintains high reactivity over the entire course of HKR reactions. We describe here an investigation of catalyst partitioning with different (salen)Co-X precatalysts and demonstrate that counterion addition to epoxide is reversible in the case of the (salen)Co-OTs. This reversible counterion addition results in stable partitioning between nucleophilic and Lewis acidic catalyst species, allowing highly efficient catalysis throughout the course of the HKR reaction.
Figures







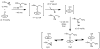

References
-
- Tokunaga M, Larrow JF, Kakiuchi F, Jacobsen EN. Science. 1997;277:936–938. - PubMed
- Schaus SE, Brandes BD, Larrow JF, Tokunaga M, Hansen KB, Gould AE, Furrow ME, Jacobsen EN. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:1307–1315. - PubMed
- Larrow JF, Hemberger KE, Jasmin S, Kabir H, Morel P. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2003;14:3589–2592.
- Stevenson CP, Nielsen LPC, Jacobsen EN, McKinley JD, White TD, Couturier MA, Ragan J. Org Synth. 2006;83:162–169.
-
-
For recent reviews of applications of the HKR reaction in industrial and natural products synthesis, see: Kumar P, Naidu V, Gupta P. Tetrahedron. 2007;63:2745–2785.Furukawa Y, Suzuki T, Mikami M, Kitaori K, Yoshimoto H. J Synth Org Chem Japan. 2007;65:308–319.Kumar P, Gupta P. Synlett. 2009:1367–1382.
-
-
-
Phenols: Ready JM, Jacobsen EN. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:6086–6087.Carbamates: Bartoli G, Bosco M, Carlone A, Locatelli M, Melchiorre P, Sambri L. Org Lett. 2004;22:3973–3975.Azides: Martínez LE, Leighton JL, Carsten DH, Jacobsen EN. J Am Chem Soc. 1995;117:5897–5898.Anilines: Bartoli G, Bosco M, Carlone A, Locatelli M, Massaccesi M, Melchiorre P, Sambri L. Org Lett. 2004;6:2173–2176.Indoles: Bandini M, Cozzi PG, Melchiorre P, Umani-Ronchi A. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:84–87.
-
-
-
For reviews see: Jacobsen EN. Acc Chem Res. 2000;33:421–431.Nielsen LPC, Jacobsen EN. In: In Aziridines and Epoxides in Organic Synthesis. Yudin AK, editor. Chapter 7 Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 2006.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

