Basal cell carcinoma - molecular biology and potential new therapies
- PMID: 22293184
- PMCID: PMC3266783
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58779
Basal cell carcinoma - molecular biology and potential new therapies
Abstract
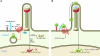
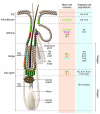
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) of the skin, the most common malignancy in individuals of mixed European descent, is increasing in incidence due to an aging population and sun exposure habits. The realization that aberrant activation of Hedgehog signaling is a pathognomonic feature of BCC development has opened the way for exciting progress toward understanding BCC biology and translation of this knowledge to the clinic. Genetic mouse models closely mimicking human BCCs have provided answers about the tumor cell of origin, and inhibition of Hedgehog signaling is emerging as a potentially useful targeted therapy for patients with advanced or multiple BCCs that have hitherto lacked effective treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Jacob A. Observations respecting an ulcer of peculiar character, which attacks the eyelids and other parts of the face. Dublin Hospital Rep Commun Med Surg. 1827;4:232–239.
-
- Krompecher E. Der drüsenartige Oberflachenepithelkrebs. Carcinoma epi- theliale adenoides. Beitr z path Anat u z adg Path. 1900;28:1–41.
-
- Krompecher E.Der Basalzellenkrebs. Jena: Gustav Fischer; 1903.
-
- Mallory FB. Recent progress in the microscopic anatomy and differentiation of cancer. JAMA. 1910. 55 18 1513 1516 . 10.1001/jama.1910.04330180001001 - DOI
-
- Ten Seldam REJ, Helwig EB.Histological Typing Of Skin Tumours . Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1974.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

