Rac1 gets fattier
- PMID: 22293830
- PMCID: PMC3273399
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.481
Rac1 gets fattier
Abstract
EMBO J 31 3, 534–551 (2012); published online December 09 2011
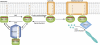
Since its description more than two decades ago as a substrate for botulinum C3 exoenzyme (Didsbury et al, 1989), Rac1 has been one of the most studied small GTPases of the Ras superfamily. Interest in Rac1 exploded in 1992 when Ridley and Hall published their seminal work showing that Rac1 regulates the actin cytoskeleton to promote lamellipodia formation (Ridley et al, 1992). Since that report, >4350 studies have been published on Rac1 and seemingly every detail of its regulation and biological function has been dissected, including its post-translational modifications. It therefore comes as somewhat of a surprise when del Pozo and colleagues (Navarro-Lérida et al, 2012) report for the first time in this issue of The EMBO Journal that Rac1 can be palmitoylated and that acylation directs its location in plasma membrane microdomains and modulates its signalling output.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chiu VK, Bivona T, Hach A, Sajous JB, Silletti J, Wiener H, Johnson RL II, Cox AD, Philips MR (2002) Ras signalling on endoplasmic recticulum and Golgi. Nat Cell Biol 4: 343–350 - PubMed
-
- Choy E, Chiu VK, Silletti J, Feoktistov M, Morimoto T, Michaelson D, Ivanov IE, Philips MR (1999) Endomembrane trafficking of ras: the CAAX motif targets proteins to the ER and Golgi. Cell 98: 69–80 - PubMed
-
- del Pozo MA, Alderson NB, Kiosses WB, Chiang H-H, Anderson RGW, Schwartz MA (2004) Integrins regulate Rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains. Science (New York, NY) 303: 839–842 - PubMed
-
- Didsbury J, Weber RF, Bokoch GM, Evans T, Snyderman R (1989) rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem 264: 16378–16382 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

