Microwave-assisted synthesis of new substituted anilides of quinaldic acid
- PMID: 22293847
- PMCID: PMC6268041
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17021292
Microwave-assisted synthesis of new substituted anilides of quinaldic acid
Abstract
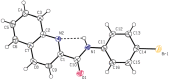
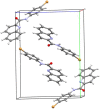
In this study a one step method for the preparation of substituted anilides of quinoline-2-carboxylic acid was developed. This efficient innovative approach is based on the direct reaction of an acid or ester with substituted anilines using microwave irradiation. The optimized method was used for the synthesis of a series of eighteen substituted quinoline-2-carboxanilides. The molecular structure of N-(4-bromophenyl)quinoline-2-carboxamide as a model compound was determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. It crystallizes in the monoclinic space group with four molecules within the unit cell and the total structure of the compound can be described as "a slightly screwed boat".
Figures
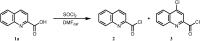

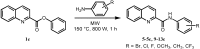
References
-
- Kharkar P.S., Deodhar M.N., Kulkarni V.M. Design, synthesis, antifungal activity, and ADME prediction of functional analogues of terbinafine. Med. Chem. Res. 2009;18:421–432.
-
- Musiol R., Serda M., Hensel-Bielowka S., Polanski J. Quinoline-based antifungals. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010;17:1960–1973. - PubMed
-
- Nakamoto K., Tsukada I., Tanaka K., Matsukura M., Haneda T., Inoue S., Murai N., Abe S., Ueda N., Miyazaki M., et al. Synthesis and evaluation of novel antifungal agents-quinoline and pyridine amide derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010;20:4624–4626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

