Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence by increasing hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 22294162
- PMCID: PMC3577350
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.895
Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence by increasing hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
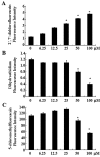
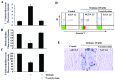
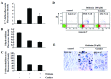
We recently demonstrated that oridonin could induce apoptosis and senescence of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. However, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. In this study, the involvement of reactive oxygen species in oridonin-induced cell death and senescence was investigated in colon adenocarcinoma-derived SW1116 cells. Oridonin increased intracellular hydrogen peroxide levels and reduced the glutathione content in a dose-dependent manner. N-acetylcysteine, a reactive oxygen species scavenger, not only blocked the oridonin-induced increase in hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion, but also blocked apoptosis and senescence induced by oridonin, as evidenced by the decrease in Annexin V and senescence-associated β-galactosidase- positive cells and the inhibition of oridonin-induced upregulation of p53 and p16 and downregulation of c-Myc. Moreover, exogenous catalase could inhibit the increase in hydrogen peroxide and apoptosis induced by oridonin, but not the glutathione depletion and senescence. Furthermore, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) activity was reduced by oridonin in vitro and in cells, which may cause the increase in hydrogen peroxide. In conclusion, the increase in hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion account for oridonin-induced apoptosis and senescence in colorectal cancer cells, and TrxR inhibition is involved in this process. Given the importance of TrxR as a novel cancer target in colon cancer, oridonin would be a promising clinical candidate. The mechanism of oridonin-induced inhibition of TrxR warrants further investigation.
Figures

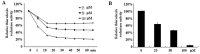
Similar articles
-
Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence in colorectal cancer cells by increasing histone hyperacetylation and regulation of p16, p21, p27 and c-myc.BMC Cancer. 2010 Nov 6;10:610. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-610. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21054888 Free PMC article.
-
Oridonin Induces Oxidative Stress-mediated Cancer Cells Apoptosis via Targeting Thioredoxin Reductase.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(14):1647-1657. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666211217151955. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34923938
-
Hydroxyl radical (·OH) played a pivotal role in oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(12):2148-59. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00405. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 23207767
-
ROS/JNK/c-Jun axis is involved in oridonin-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jun 4;513(3):594-601. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30981511
-
Intracellular glutathione depletion by oridonin leads to apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells.Molecules. 2014 Mar 18;19(3):3327-44. doi: 10.3390/molecules19033327. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24647034 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oridonin induces Mdm2-p60 to promote p53-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in neuroblastoma.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(11):5313-5326. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2393. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31339234 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing cancer therapy: advanced nanovehicle delivery systems for oridonin.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 3;15:1476739. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1476739. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39691396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis-modulating small molecules for targeting drug-resistant cancer: Challenges and opportunities in manipulating redox signaling.Med Res Rev. 2023 May;43(3):614-682. doi: 10.1002/med.21933. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Med Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36658724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Oridonin and Its Analogs: From Anticancer and Antiinflammation to Neuroprotection.Molecules. 2018 Feb 22;23(2):474. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020474. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29470395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of ROS-Mediated Oridonin-Induced Oesophageal Cancer KYSE-150 Cell Apoptosis by Atomic Force Microscopy.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 23;10(10):e0140935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140935. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26496199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonzalez C, Sanz-Alfayate G, Agapito MT, Gomez-Nino A, Rocher A, Obeso A. Significance of ROS in oxygen sensing in cell systems with sensitivity to physiological hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2002;132:17–41. - PubMed
-
- Baran CP, Zeigler MM, Tridandapani S, Marsh CB. The role of ROS and RNS in regulating life and death of blood monocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:855–866. - PubMed
-
- Yamada J, Yoshimura S, Yamakawa H, et al. Cell permeable ROS scavengers, Tiron and Tempol, rescue PC12 cell death caused by pyrogallol or hypoxia/reoxygenation. Neurosci Res. 2003;45:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi A, Ohtani N, Yamakoshi K, et al. Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a-Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1291–1297. - PubMed
-
- Mena S, Ortega A, Estrela JM. Oxidative stress in environmental-induced carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 2009;674:36–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

