Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence by increasing hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 22294162
- PMCID: PMC3577350
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.895
Oridonin induces apoptosis and senescence by increasing hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
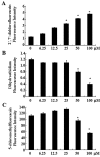
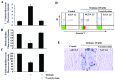
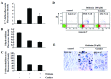
We recently demonstrated that oridonin could induce apoptosis and senescence of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. However, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. In this study, the involvement of reactive oxygen species in oridonin-induced cell death and senescence was investigated in colon adenocarcinoma-derived SW1116 cells. Oridonin increased intracellular hydrogen peroxide levels and reduced the glutathione content in a dose-dependent manner. N-acetylcysteine, a reactive oxygen species scavenger, not only blocked the oridonin-induced increase in hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion, but also blocked apoptosis and senescence induced by oridonin, as evidenced by the decrease in Annexin V and senescence-associated β-galactosidase- positive cells and the inhibition of oridonin-induced upregulation of p53 and p16 and downregulation of c-Myc. Moreover, exogenous catalase could inhibit the increase in hydrogen peroxide and apoptosis induced by oridonin, but not the glutathione depletion and senescence. Furthermore, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) activity was reduced by oridonin in vitro and in cells, which may cause the increase in hydrogen peroxide. In conclusion, the increase in hydrogen peroxide and glutathione depletion account for oridonin-induced apoptosis and senescence in colorectal cancer cells, and TrxR inhibition is involved in this process. Given the importance of TrxR as a novel cancer target in colon cancer, oridonin would be a promising clinical candidate. The mechanism of oridonin-induced inhibition of TrxR warrants further investigation.
Figures

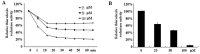
References
-
- Gonzalez C, Sanz-Alfayate G, Agapito MT, Gomez-Nino A, Rocher A, Obeso A. Significance of ROS in oxygen sensing in cell systems with sensitivity to physiological hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2002;132:17–41. - PubMed
-
- Baran CP, Zeigler MM, Tridandapani S, Marsh CB. The role of ROS and RNS in regulating life and death of blood monocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:855–866. - PubMed
-
- Yamada J, Yoshimura S, Yamakawa H, et al. Cell permeable ROS scavengers, Tiron and Tempol, rescue PC12 cell death caused by pyrogallol or hypoxia/reoxygenation. Neurosci Res. 2003;45:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi A, Ohtani N, Yamakoshi K, et al. Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a-Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1291–1297. - PubMed
-
- Mena S, Ortega A, Estrela JM. Oxidative stress in environmental-induced carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 2009;674:36–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

