The association of statins and taxanes: an efficient combination trigger of cancer cell apoptosis
- PMID: 22294184
- PMCID: PMC3322964
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.6
The association of statins and taxanes: an efficient combination trigger of cancer cell apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Cancer cell killing might be achieved by the combined use of available drugs. Statins are major anti-hypercholesterolemia drugs, which also trigger apoptosis of many cancer cell types, while docetaxel is a potent microtubule-stabilising agent.
Methods: Here, we looked at the combined effects of lovastatin and docetaxel in cancer cells.
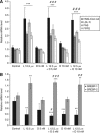
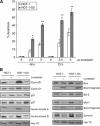
Results: Whole transcriptome microarrays in HGT-1 gastric cancer cells demonstrated that lovastatin strongly suppressed expression of genes involved in cell division, while docetaxel had very little transcriptional effects. Both drugs triggered apoptosis, and their combination was more than additive. A marked rise in the cell-cycle inhibitor p21, together with reduction of aurora kinases A and B, cyclins B1 and D1 proteins was induced by lovastatin alone or in combination with docetaxel. The drug treatments induced the proteolytic cleavage of procaspase-3, a drop of the anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 protein, Poly-ADP-Ribose Polymerase and Bax. Strikingly, docetaxel-resistant HGT-1 cell derivatives overexpressing the MDR-1 gene were much more sensitive to lovastatin than docetaxel-sensitive cells.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the association of lovastatin and docetaxel, or lovastatin alone, shows promise as plausible anticancer strategies, either as a direct therapeutic approach or following acquired P-glycoprotein-dependent resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
HIV-1 protease inhibitor, ritonavir: a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, enhanced the anticancer effects of docetaxel in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 15;64(20):7426-31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2677. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15492266
-
Lovastatin induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells and synergizes with doxorubicin: potential therapeutic relevance.BMC Cancer. 2010 Mar 18;10:103. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-103. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20298590 Free PMC article.
-
AT9283, a novel aurora kinase inhibitor, suppresses tumor growth in aggressive B-cell lymphomas.Int J Cancer. 2012 Jun 15;130(12):2997-3005. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26324. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21796626
-
Effects of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib alone and in combination with chemotherapeutic agents in gastric cancer cell lines.Oncol Rep. 2008 Apr;19(4):1027-32. Oncol Rep. 2008. PMID: 18357392
-
Sequential combination of flavopiridol and docetaxel reduces the levels of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis and AKT proteins and stimulates apoptosis in human LNCaP prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 May;5(5):1216-26. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0467. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16731754
Cited by
-
Repurposed Drugs in Gastric Cancer.Molecules. 2022 Dec 30;28(1):319. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010319. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Gastric Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 15;12:916661. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.916661. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atorvastatin inhibits the proliferation of MKN45-derived gastric cancer stem cells in a mevalonate pathway-independent manner.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 1;26(5):367-375. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.5.367. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36039737 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Statin Use and Gastric Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort in Korea.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;14(12):1283. doi: 10.3390/ph14121283. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959682 Free PMC article.
-
Momordica charantia lectin exhibits antitumor activity towards hepatocellular carcinoma.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Feb;33(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0156-8. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25200916
References
-
- Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, Moss SF, Ramey WG, Holt PR (1999) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5(8): 2223–2229 - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA (2008) Optimizing docetaxel chemotherapy in patients with cancer of the gastric and gastroesophageal junction: evolution of the docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil regimen. Cancer 113(5): 945–955 - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Ajani J, Scotte F, Winther D, Martin M, Aapro MS, von Minckwitz G (2009) Docetaxel-related side effects and their management. Eur J Oncol Nurs 13(1): 49–59 - PubMed
-
- Berchem GJ, Bosseler M, Mine N, Avalosse B (1999) Nanomolar range docetaxel treatment sensitizes MCF-7 cells to chemotherapy induced apoptosis, induces G2M arrest and phosphorylates bcl-2. Anticancer Res 19(1A): 535–540 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

