Advances in lead-free piezoelectric materials for sensors and actuators
- PMID: 22294907
- PMCID: PMC3264460
- DOI: 10.3390/s100301935
Advances in lead-free piezoelectric materials for sensors and actuators
Abstract
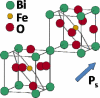
Piezoelectrics have widespread use in today's sensor and actuator technologies. However, most commercially available piezoelectric materials, e.g., Pb [Zr(x)Ti(1-x)] O(3) (PZT), are comprised of more than 60 weight percent lead (Pb). Due to its harmful effects, there is a strong impetus to identify new lead-free replacement materials with comparable properties to those of PZT. This review highlights recent developments in several lead-free piezoelectric materials including BaTiO(3), Na(0.5)Bi(0.5)TiO(3), K(0.5)Bi(0.5)TiO(3), Na(0.5)K(0.5)NbO(3), and their solid solutions. The factors that contribute to strong piezoelectric behavior are described and a summary of the properties for the various systems is provided.
Keywords: ceramics; electromechanical; ferroelectrics; piezoelectrics.
Figures








References
-
- Setter N. ABC of piezoelectricity and piezoelectric materials. In: Setter N., editor. Piezoelectric Materials in Devices. Nava Setter; Lausanne, Switzerland: 2002. p. 518.
-
- Cross E. Materials science-Lead-free at last. Nature. 2004;432:24–25. - PubMed
-
- Saito Y., Takao H., Tani T., Nonoyama T., Takatori K., Homma T., Nagaya T., Nakamura M. Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature. 2004;432:84–87. - PubMed
-
- Haertling G.H. Ferroelectric ceramics: history and technology. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 1999;82:797–818.
-
- Viehland D. Effect of uniaxial stress upon the electromechanical properties of various piezoelectric ceramics and single crystals. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 2006;89:775–785.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

