Upper extremity surgery in younger children under ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block: a case series
- PMID: 22295045
- PMCID: PMC3024489
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-010-0303-5
Upper extremity surgery in younger children under ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block: a case series
Abstract
Purpose: Supraclavicular brachial plexus block is considered to be one of the most effective anesthetic procedures for upper extremity surgeries. Its major drawback is placement of the needle, with inaccurate placement, especially in children, being a risk factor for pneumothorax and vascular puncture and failure of the procedure. Ultrasound-guided needle placement may reduce the risk of complications and increase the accuracy of the block, particularly in pediatric patients. Little has been published on the efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block in children based on practical experience, and there has been no published report on its usage in younger children (<6 years old).
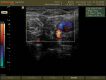
Methods: Seventeen patients between the ages of 6 months and 6 years were randomly selected to test the efficacy of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block in younger children. The ultrasound probe was used for proper placement of the needle. After confirmation of the needle location using a nerve locator, the anesthetic agent was injected. The procedure time, establishment time, duration of analgesia, any complications related to the procedure, and surgeon's satisfaction were recorded and assessed.
Results: The length of the procedure was 10.35 ± 1.22 min, establishment time was 89.59 + 18 s, and the duration of the analgesia was between 6 and 16 h (mean 9.76 ± 2.57 h). The recovery time was 24.4 + 6.5 min (range 15-37 min), and the duration of surgeries was 61.3 ± 25.9 min (range 15-110 min). Not one procedure failed, and there was not one complication related to the procedure. The surgeon's satisfaction during surgery was good or excellent.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrate the efficacy and safety of the ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block for orthopedic upper extremity surgeries in patients less than 6 years of age.
Keywords: Brachial plexus block; Pediatric anesthesia; Pediatric upper extremity surgery; Regional anesthesia; Supraclavicular; Ultrasound.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

