Alternate estrogen receptors promote invasion of inflammatory breast cancer cells via non-genomic signaling
- PMID: 22295107
- PMCID: PMC3266301
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030725
Alternate estrogen receptors promote invasion of inflammatory breast cancer cells via non-genomic signaling
Abstract
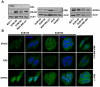
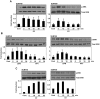
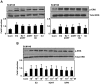
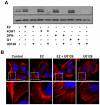
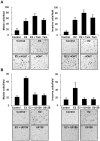
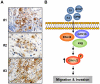
Although Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) is a rare and an aggressive type of locally advanced breast cancer with a generally worst prognosis, little work has been done in identifying the status of non-genomic signaling in the invasiveness of IBC. The present study was performed to explore the status of non-genomic signaling as affected by various estrogenic and anti-estrogenic agents in IBC cell lines SUM149 and SUM190. We have identified the presence of estrogen receptor α (ERα) variant, ERα36 in SUM149 and SUM190 cells. This variant as well as ERβ was present in a substantial concentration in IBC cells. The treatment with estradiol (E2), anti-estrogenic agents 4-hydroxytamoxifen and ICI 182780, ERβ specific ligand DPN and GPR30 agonist G1 led to a rapid activation of p-ERK1/2, suggesting the involvement of ERα36, ERβ and GPR30 in the non-genomic signaling pathway in these cells. We also found a substantial increase in the cell migration and invasiveness of SUM149 cells upon the treatment with these ligands. Both basal and ligand-induced migration and invasiveness of SUM149 cells were drastically reduced in the presence of MEK inhibitor U0126, implicating that the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 by MEK is involved in the observed motility and invasiveness of IBC cells. We also provide evidence for the upregulation of p-ERK1/2 through immunostaining in IBC patient samples. These findings suggest a role of non-genomic signaling through the activation of p-ERK1/2 in the hormonal dependence of IBC by a combination of estrogen receptors. These findings only explain the failure of traditional anti-estrogen therapies in ER-positive IBC which induces the non-genomic signaling, but also opens newer avenues for design of modified therapies targeting these estrogen receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in modulating urothelial cell proliferation.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008 Mar;15(1):351-64. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01255. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18310301 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM1) overexpression enhances the aggressive phenotype of SUM149 inflammatory breast cancer cells in a signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 (STAT2)-dependent manner.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 20;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0683-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26897526 Free PMC article.
-
Raloxifene induces cell death and inhibits proliferation through multiple signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells expressing different levels of estrogen receptor α and β.J Cell Physiol. 2011 May;226(5):1334-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22461. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20945400
-
New Treatment Strategies for the Inflammatory Breast Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021 Apr 24;22(6):50. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00843-2. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33893888 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor β and Liver X receptor β: biology and therapeutic potential in CNS diseases.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Feb;20(1):18-22. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.23. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24662928 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytoplasmic kinases downstream of GPR30 suppress gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)-induced luteinizing hormone secretion from bovine anterior pituitary cells.J Reprod Dev. 2016;62(1):65-9. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2015-104. Epub 2015 Oct 30. J Reprod Dev. 2016. PMID: 26522383 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding estrogen receptor and GPER biology: structural insights and therapeutic advances in ERα-positive breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 26;15:1513225. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1513225. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40641933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bisphenol A activates EGFR and ERK promoting proliferation, tumor spheroid formation and resistance to EGFR pathway inhibition in estrogen receptor-negative inflammatory breast cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Mar 1;38(3):252-260. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx003. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28426875 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Lipocalin-2 in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells with Small Interference RNA and Small Molecule Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 10;22(16):8581. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168581. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445288 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ER-α36 in breast cancer by typical xenoestrogens.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):7355-64. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4006-x. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26337277 Review.
References
-
- Dirix LY, Van Dam P, Prové A, Vermeulen PB. Inflammatory breast cancer: current understanding. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18:563–571. - PubMed
-
- Merajver SD, Weber BL, Cody R, Zhang D, Strawderman M, et al. Breast conservation and prolonged chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer: the University of Michigan experience. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2873–2881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

