Involvement of Rho kinase (ROCK) in sepsis-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 22295165
- PMCID: PMC3256549
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2010.08.04
Involvement of Rho kinase (ROCK) in sepsis-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
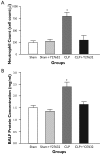
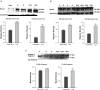
Indirect acute lung injury is associated with high morbidity and mortality. We investigated the link between Rho kinase (ROCK) activation and apoptotic cell death in sepsis induced acute lung injury. This hypothesis was tested by administering a specific, selective inhibitor of ROCK (Y-27632) to rats subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Rats were randomly divided into 4 groups as; sham-operated, sham + Y-27632, CLP and CLP + Y-27632. Twenty-four hours later, each experiment was terminated and lungs analyzed. Histopathology was assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and the presence of apoptosis was evaluated through the TUNEL assay. Pulmonary activity of caspase 3 and ROCK 1 & 2 were measured by western blot. Interstitial edema, severely damaged pulmonary architecture with massive infiltration of the inflammatory cells and an increase in lung tissue TBARS levels as well as 3-NT to total tyrosine ratios were observed in untreated CLP animals. Pretreatment of animals with Y-27632, reduced lung injury in the CLP induced septic rats in each of these parameters of lung injury (p<0.05). Western immunoblot revealed active caspase cleavage and increased expression of active fragment of ROCK 1 & 2 in the CLP group. TUNEL assay showed an increase in percentage of apoptotic cells when comparing the CLP group with the CLP + Y-27632 group. These results suggest an important role of Rho kinase in sepsis induced lung injury by a mechanism that might be related to oxidative and/or nitrosative stress mediated caspase cleavage leading to apoptosis.
Keywords: 3-Nitrotyrosine; ROCK; Rho kinase; Sepsis; acute lung injury; apoptosis; nitric oxide; peroxynitrite; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Angus DC, Wax RS. Epidemiology of sepsis: an update. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:S109–16. - PubMed
-
- Cinel I, Dellinger RP. Advances in pathogenesis and management of sepsis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20:345–52. - PubMed
-
- Cinel I, Opal SM. Molecular biology of inflammation and sepsis: a primer. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:291–304. - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, et al. Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1230–51. - PubMed
-
- Cinel I, Buyukafsar K, Cinel L, Polat A, Atici S, Tamer L, et al. The role of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibition in preventing endotoxemia-induced intestinal epithelial apoptosis. Pharmacol Res. 2002;46:119–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
