Pea Albumin 1 subunit b (PA1b), a promising bioinsecticide of plant origin
- PMID: 22295174
- PMCID: PMC3268454
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins3121502
Pea Albumin 1 subunit b (PA1b), a promising bioinsecticide of plant origin
Abstract
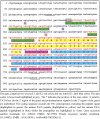
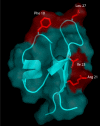
PA1b (Pea Albumin 1, subunit b) is a peptide extract from pea seeds showing significant insecticidal activity against certain insects, such as cereal weevils (genus Sitophilus), the mosquitoes Culex pipiens and Aedes aegyptii, and certain species of aphids. PA1b has great potential for use on an industrial scale and for use in organic farming: it is extracted from a common plant; it is a peptide (and therefore suitable for transgenic applications); it can withstand many steps of extraction and purification without losing its activity; and it is present in a seed regularly consumed by humans and mammals without any known toxicity or allergenicity. The potential of this peptide to limit pest damage has stimulated research concerning its host range, its mechanism of action, its three-dimensional structure, the natural diversity of PA1b and its structure-function relationships.
Keywords: PA1b; Legumes; bioinsecticide; insect.
Figures
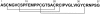


Similar articles
-
The interaction of the bioinsecticide PA1b (Pea Albumin 1 subunit b) with the insect V-ATPase triggers apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 7;7(1):4902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05315-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28687751 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and biological activity of the cystine knot bioinsecticide PA1b (Pea Albumin 1 Subunit b).PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e81619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081619. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349099 Free PMC article.
-
PA1b, an insecticidal protein extracted from pea seeds (Pisum sativum): 1H-2-D NMR study and molecular modeling.Biochemistry. 2003 Oct 21;42(41):11915-23. doi: 10.1021/bi034803l. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14556622
-
Receptors of garlic (Allium sativum) lectins and their role in insecticidal action.Protein J. 2012 Aug;31(6):439-46. doi: 10.1007/s10930-012-9423-8. Protein J. 2012. PMID: 22623282 Review.
-
Radioligand Recognition of Insecticide Targets.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Apr 4;66(13):3277-3290. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05984. Epub 2018 Mar 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29522334 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Gastrointestinal Stable Pea Albumin Nanomicelles for Capsaicin Delivery and Their Effects for Enhanced Mucus Permeability at Small Intestine.Biomater Res. 2024 Aug 16;28:0065. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0065. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39157812 Free PMC article.
-
Hijacking of N-fixing legume albumin-1 genes enables the cyclization and stabilization of defense peptides.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 3;15(1):6565. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50742-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39095373 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of the bioinsecticide PA1b (Pea Albumin 1 subunit b) with the insect V-ATPase triggers apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 7;7(1):4902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05315-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28687751 Free PMC article.
-
Aphid BCR4 Structure and Activity Uncover a New Defensin Peptide Superfamily.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12480. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012480. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293341 Free PMC article.
-
The Archetypal Gamma-Core Motif of Antimicrobial Cys-Rich Peptides Inhibits H+-ATPases in Target Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 6;25(17):9672. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179672. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bednarek P., Osbourn A. Plant-microbe interactions: Chemical diversity in plant defense. Science. 2009;324:746–748. - PubMed
-
- Delobel B., Grenier A.M. Effect of noncereal food on cereal weevils and tamarind pod weevil (coleoptera, curculionidae) J. Stored Prod. Res. 1993;29:7–14.
-
- Delobel B., Grenier A.M., Gueguen J., Ferrasson E., Mbaiguinam M. Utilisation d’un polypeptide dérivé d’une albumine PA1b de légumineuse comme insecticide. FR Patent Brevet 98/05877. 1998
-
- Higgins T.J., Chandler P.M., Randall P.J., Spencer D., Beach L.R., Blagrove R.J., Kortt A.A., Inglis A.S. Gene structure, protein structure, and regulation of the synthesis of a sulfur-rich protein in pea seed. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:11124–11130. - PubMed
-
- Jouvensal L., Quillien L., Ferrasson E., Rahbe Y., Gueguen J., Vovelle F. PA1b, an insecticidal protein extracted from pea seeds (Pisum sativum): 1H-2-D NMR study and molecular modeling. Biochemistry. 2003;42:11915–11923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

