Lymphangiogenesis and Axillary Lymph Node Metastases Correlated with VEGF-C Expression in Two Immunocompetent Mouse Mammary Carcinoma Models
- PMID: 22295235
- PMCID: PMC3262555
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/867152
Lymphangiogenesis and Axillary Lymph Node Metastases Correlated with VEGF-C Expression in Two Immunocompetent Mouse Mammary Carcinoma Models
Abstract
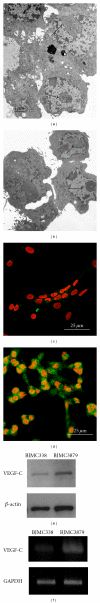
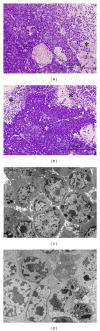
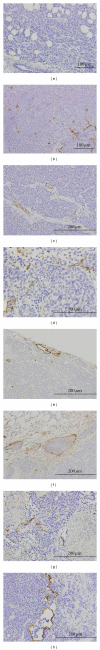
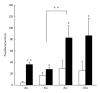
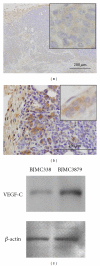
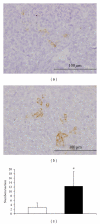
Lymphangiogenesis and the expression of vascular endothelial cell growth factor C (VEGF-C) in tumors have been considered to be causally promoting lymphatic metastasis. There are only a few studies on lymphatic metastasis in immunocompetent allograft mouse models. To study the relationship between VEGF-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis and axillary lymph node metastasis, we used two mouse mammary carcinoma cell lines; the BJMC338 has a low metastatic propensity, whereas the BJMC3879 has a high metastatic propensity although it originated from the former cell line. Each cell line was injected separately into two groups of female BALB/c mice creating in vivo mammary cancer models. The expression level of VEGF-C in BJMC3879 was higher than BJMC338. As the parent cell line, BJMC3879-derived tumors showed higher expression of VEGF-C compared to BJMC338-derived tumors. This higher expression of VEGF-C in BJMC3879-derived tumors was associated with marked increase in infiltrating macrophages and enhanced expression of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1) reflecting increased tumoral lymphatic density and subsequent induction of axillary lymph node metastasis. Our mouse mammary carcinoma models are allotransplanted tumors showing the same axillary lymph node metastatic spectrum as human breast cancers. Therefore, our mouse models are ideal for exploring the various molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis.
Figures


References
-
- Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Studer P, Breiteneder-Geleff S. Lymphatic microvessel density and lymphovascular invasion assessed by anti-podoplanin immunostaining in human breast cancer. Anticancer Research. 2001;21(4):2351–2355. - PubMed
-
- Bono P, Wasenius VM, Heikkilä P, Lundin J, Jackson DG, Joensuu H. High LYVE-1-positive lymphatic vessel numbers are associated with poor outcome in breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2004;10(21):7144–7149. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, et al. Lymph vessel density correlates with nodal status, VEGF-C expression, and prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2005;91(2):125–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

