The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in the Organ Tropism of Breast Cancer Metastasis: A Mechanistic Balance between the "Seed" and the "Soil"?
- PMID: 22295241
- PMCID: PMC3262605
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/209748
The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in the Organ Tropism of Breast Cancer Metastasis: A Mechanistic Balance between the "Seed" and the "Soil"?
Abstract
Breast cancer is a prevalent disease worldwide, and the majority of deaths occur due to metastatic disease. Clinical studies have identified a specific pattern for the metastatic spread of breast cancer, termed organ tropism; where preferential secondary sites include lymph node, bone, brain, lung, and liver. A rare subpopulation of tumor cells, the cancer stem cells (CSCs), has been hypothesized to be responsible for metastatic disease and therapy resistance. Current treatments are highly ineffective against metastatic breast cancer, likely due to the innate therapy resistance of CSCs and the complex interactions that occur between cancer cells and their metastatic microenvironments. A better understanding of these interactions is essential for the development of novel therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. This paper summarizes the characteristics of breast CSCs and their potential metastatic microenvironments. Furthermore, it raises the question of the existence of a CSC niche and highlights areas for future investigation.
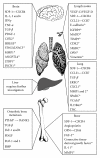
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer stem cells promote lymph nodes metastasis of breast cancer by reprogramming tumor microenvironment.Transl Oncol. 2023 Sep;35:101733. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101733. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37421907 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Lung: Clinical and Experimental Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 8;20(9):2272. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092272. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31071959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Cancer Stem Cells as Drivers of Tumor Chemoresistance, Dormancy and Relapse: New Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 15;11(10):1569. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101569. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31619007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle Delivery of TWIST Small Interfering RNA and Anticancer Drugs: A Therapeutic Approach for Combating Cancer.Enzymes. 2018;44:83-101. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2018.08.004. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Enzymes. 2018. PMID: 30360816 Review.
-
Interplay of Stem Cell Characteristics, EMT, and Microtentacles in Circulating Breast Tumor Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2013 Nov 14;5(4):1545-65. doi: 10.3390/cancers5041545. Cancers (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24240660 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Modulation of SOX2 expression delineates an end-point for paclitaxel-effectiveness in breast cancer stem cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 23;7(1):9170. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08971-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28835684 Free PMC article.
-
Seed, soil, and beyond: The basic biology of brain metastasis.Surg Neurol Int. 2013 May 2;4(Suppl 4):S256-64. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.111303. Print 2013. Surg Neurol Int. 2013. PMID: 23717797 Free PMC article.
-
The PIK3CA gene and its pivotal role in tumor tropism of triple-negative breast cancer.Transl Oncol. 2024 Dec;50:102140. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102140. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39369580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung-derived factors mediate breast cancer cell migration through CD44 receptor-ligand interactions in a novel ex vivo system for analysis of organ-specific soluble proteins.Neoplasia. 2014 Feb;16(2):180-91. doi: 10.1593/neo.132076. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 24709425 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression in "young adult type" breast cancer: a retrospective analysis.Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13688-702. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4051. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25999348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canadian Cancer Society's Steering Committee. Canadian Cancer Statistics 2011. Toronto, Canada: Canadian Cancer Society; 2011.
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2011;61(4):212–236. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. International Journal of Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Key TJ, Verkasalo PK, Banks E. Epidemiology of breast cancer. Lancet Oncology. 2001;2(3):133–140. - PubMed
-
- Porter PL. Global trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality. Salud Pública de México. 2009;51(supplement 2):s141–s146. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

