Late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance predicts clinical worsening in patients with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 22296860
- PMCID: PMC3311144
- DOI: 10.1186/1532-429X-14-11
Late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance predicts clinical worsening in patients with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
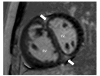
Background: Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) occurs at the right ventricular (RV) insertion point (RVIP) in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) and has been shown to correlate with cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) derived RV indices. However, the prognostic role of RVIP-LGE and other CMR-derived parameters of RV function are not well established. Our aim was to evaluate the predictive value of contrast-enhanced CMR in patients with PH.
Methods: RV size, ejection fraction (RVEF), and the presence of RVIP-LGE were determined in 58 patients with PH referred for CMR. All patients underwent right heart catheterization, exercise testing, and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) evaluation; results of which were included in the final analysis if performed within 4 months of the CMR study. Patients were followed for the primary endpoint of time to clinical worsening (death, decompensated right ventricular heart failure, initiation of prostacyclin, or lung transplantation).
Results: Overall, 40/58 (69%) of patients had RVIP-LGE. Patients with RVIP- LGE had larger right ventricular volume index, lower RVEF, and higher mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP), all p < 0.05. During the follow-up period of 10.2 ± 6.3 months, 19 patients reached the primary endpoint. In a univariate analysis, RVIP-LGE was a predictor for adverse outcomes (p = 0.026). In a multivariate analysis, CMR-derived RVEF was an independent predictor of clinical worsening (p = 0.036) along with well-established prognostic parameters such as exercise capacity (p = 0.010) and mPAP (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: The presence of RVIP-LGE in patients with PH is a marker for more advanced disease and poor prognosis. In addition, this study reveals for the first time that CMR-derived RVEF is an independent non-invasive imaging predictor of adverse outcomes in this patient population.
© 2012 Freed et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, Fishman AP, Goldring RM, Groves BM, Kernis JT, Levy PS, Pietra GG, Reid LM, Reeves JT, Rich S, Vreim CE, Williams GW, Wu M. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:343–9. - PubMed
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Gomberg-Maitland M. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from the registry to evaluate early and long-term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management (REVEAL) Circulation. 2010;122:164–172. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.898122. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

