Calcium balance in normal individuals and in patients with chronic kidney disease on low- and high-calcium diets
- PMID: 22297674
- PMCID: PMC3352985
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.490
Calcium balance in normal individuals and in patients with chronic kidney disease on low- and high-calcium diets
Abstract
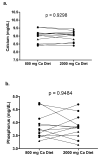
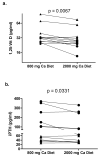
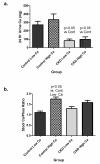
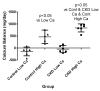
Calcium balance in chronic kidney disease is poorly understood as calcium deficiency is a stimulus for secondary hyperparathyroidism and consequent bone loss while calcium excess promotes extraosseous calcifications. To help resolve this, we evaluated calcium balance in normal individuals and in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on daily diets containing 800 and 2000 mg elemental calcium. Both normal individuals and patients with late stage 3 and stage 4 CKD were in slightly negative to neutral calcium balance on the 800-mg calcium diet. Normal individuals were in modest positive calcium balance on the 2000-mg diet, while patients with CKD on the same diet were in marked positive calcium balance at least over the 9 days of study; and significantly greater than the normal individuals. Increased calcium intake significantly decreased 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D and intact parathyroid hormone levels but did not alter the serum calcium concentration. Thus, our findings have important implications for both preventing calcium deficiency and loading in individuals with late stage 3 and stage 4 CKD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00974532.
Figures

Comment in
-
Calcium balance in chronic kidney disease: walking the tightrope.Kidney Int. 2012 Jun;81(11):1057-9. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.33. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22584593
References
-
- Levin A, Bakris GL, Molitch M, et al. Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;71:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Craver L, Marco MP, Martinez I, et al. Mineral metabolism parameters throughout chronic kidney disease stages 1–5: Achievement of K/DOQI target ranges. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:1171–1176. - PubMed
-
- Coburn JW, Koppel MH, Brickman AS, et al. Study of intestinal absorption of calcium in patients with renal failure. Kidney Int. 1973;3:264–272. - PubMed
-
- Perez AV, Picotto G, Carpentieri AR, et al. Minireview on regulation of intestinal calcium absorption. Digestion. 2008;77:22–34. - PubMed
-
- Hunt CD, Johnson LK. Calcium requirements: new estimations for men and women by cross-sectional statistical analysis of calcium balance data from metatolic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:1054–1063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

