Managing pain in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 22298998
- PMCID: PMC3264972
Managing pain in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
Pain is a common complaint in inflammatory bowel disease, and it has significant consequences for patients' quality of life. A thorough evaluation to determine the source of patients' pain should include clinical, laboratory, radiologic, and endoscopic assessments as indicated. Differentiating among active inflammation, secondary complications, and functional pain can be complicated. Even when all active disease is adequately treated, clinicians are often left with the difficulty of managing chronic pain. This paper will review the benefits and limitations of several commonly used treatments and promising future therapies. A suggested treatment algorithm will provide some guidance in this challenging area of inflammatory bowel disease management.
Keywords: Inflammatory bowel disease; irritable bowel syndrome; management; pain.
Figures
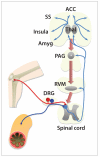
anterior cingulate cortex
amygdala
dorsal root ganglia
periaqueductal gray matter
rostroventromedial medulla
somatosensory cortex
Thalamus
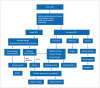
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
References
-
- Simrén M, Axelsson J, Gillberg R, et al. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease in remission: the impact of IBS-like symptoms and associated psychological factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Graff LA, Walker JR, Lix L, et al. The relationship of inflammatory bowel disease type and activity to psychological functioning and quality of life. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1491–1501. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Hanauer SB, et al. A review of activity indices and efficacy endpoints for clinical trials of medical therapy in adults with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:512–530. - PubMed
-
- De Rooy EC, Toner BB, Maunder RG, et al. Concerns of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: results from a clinical population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:1816–1821. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
