Ozone-induced lung injury and sterile inflammation. Role of toll-like receptor 4
- PMID: 22300504
- PMCID: PMC3507381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.01.004
Ozone-induced lung injury and sterile inflammation. Role of toll-like receptor 4
Abstract
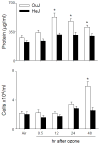
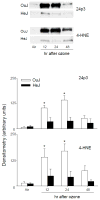
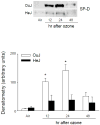
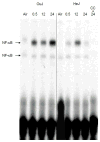
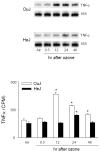
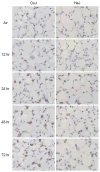
Inhalation of toxic doses of ozone is associated with a sterile inflammatory response characterized by an accumulation of macrophages in the lower lung which are activated to release cytotoxic/proinflammatory mediators that contribute to tissue injury. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a pattern recognition receptor present on macrophages that has been implicated in sterile inflammatory responses. In the present studies we used TLR4 mutant C3H/HeJ mice to analyze the role of TLR4 in ozone-induced lung injury, oxidative stress and inflammation. Acute exposure of control C3H/HeOuJ mice to ozone (0.8ppm for 3h) resulted in increases in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) lipocalin 24p3 and 4-hydroxynonenal modified protein, markers of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. This was correlated with increases in BAL protein, as well as numbers of alveolar macrophages. Levels of surfactant protein-D, a pulmonary collectin known to regulate macrophage inflammatory responses, also increased in BAL following ozone inhalation. Ozone inhalation was associated with classical macrophage activation, as measured by increased NF-κB binding activity and expression of TNFα mRNA. The observation that these responses to ozone were not evident in TLR4 mutant C3H/HeJ mice demonstrates that functional TLR4 contributes to ozone-induced sterile inflammation and macrophage activation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase B in alveolar macrophages following ozone inhalation. Role of NF-kappaB and STAT-1 in ozone-induced nitric oxide production and toxicity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 May-Jun;234-235(1-2):91-8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12162464
-
Prolonged injury and altered lung function after ozone inhalation in mice with chronic lung inflammation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;47(6):776-83. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0433OC. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22878412 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ozone-induced lung inflammation and injury by the β-galactoside-binding lectin galectin-3.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Apr 15;284(2):236-45. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25724551 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in ozone-induced lung injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;500:183-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0667-6_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 11764933 Review.
-
Ozone Exposure Controls Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Process of Hepatocytes in Murine Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;13(2):212. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020212. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping acute systemic effects of inhaled particulate matter and ozone: multiorgan gene expression and glucocorticoid activity.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Sep;135(1):169-81. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft137. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23805001 Free PMC article.
-
Acute exposure of ozone induced pulmonary injury and the protective role of vitamin E through the Nrf2 pathway in Balb/c mice.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Nov 10;5(1):268-277. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00259a. eCollection 2016 Jan 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 30090343 Free PMC article.
-
Major Effect of Oxidative Stress on the Male, but Not Female, SP-A1 Type II Cell miRNome.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1514. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01514. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31354704 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Epithelial TRPA1 Transduces the Extracellular ROS into Transcriptional Regulation of Lung Inflammation Induced by Cigarette Smoke: The Role of Influxed Ca²⁺.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:148367. doi: 10.1155/2015/148367. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26504357 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical free, nanotechnology-based method for airborne bacterial inactivation using engineered water nanostructures.Environ Sci Nano. 2014;2014(1):15-26. doi: 10.1039/C3EN00007A. Environ Sci Nano. 2014. PMID: 26180637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Andre E, Stoeger T, Takenaka S, Bahnweg M, Ritter B, Karg E, Lentner B, Reinhard C, Schulz H, Wjst M. Inhalation of ultrafine carbon particles triggers biphasic pro-inflammatory response in the mouse lung. Eur Respir J. 2006;28:275–285. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla DK. Ozone-induced lung inflammation and mucosal barrier disruption: toxicology, mechanisms, and implications. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 1999;2:31–86. - PubMed
-
- Caso JR, Pradillo JM, Hurtado O, Lorenzo P, Moro MA, Lizasoain I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in brain damage and inflammation after experimental stroke. Circulation. 2007;115:1599–1608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

