Identification of hepatitis C virus transmission using a next-generation sequencing approach
- PMID: 22301026
- PMCID: PMC3318530
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00005-12
Identification of hepatitis C virus transmission using a next-generation sequencing approach
Abstract
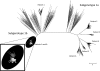
Here, we describe a transmission event of hepatitis C virus (HCV) among injection drug users. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was used to assess the intrahost viral genetic variation. Deep amplicon sequencing of HCV hypervariable region 1 allowed for a detailed analysis of the structure of the viral population. Establishment of the genetic relatedness between cases was accomplished by phylogenetic analysis. NGS is a powerful tool with applications in molecular epidemiology studies and outbreak investigations.
Figures
References
-
- Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs 2009. The primary prevention of hepatitis C among injecting drug users. Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs, London, United Kingdom
-
- Beerenwinkel N, Zagordi O. 2011. Ultra-deep sequencing for the analysis of viral populations. Curr. Opin. Virol. 1:413–418 - PubMed
-
- Boddiger D. 2010. Mexico eager to reduce demand for illicit drugs. Lancet 375:15–16 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 1998. Recommendations for prevention and control of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and HCV-related chronic disease. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 47(RR-19):1–39 - PubMed
-
- Fischer GE, et al. 2010. Hepatitis C virus infections from unsafe injection practices at an endoscopy clinic in Las Vegas, Nevada, 2007–2008. Clin. Infect. Dis. 51:267–273 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

