Interleukin-27 inhibits vaccine-enhanced pulmonary disease following respiratory syncytial virus infection by regulating cellular memory responses
- PMID: 22301139
- PMCID: PMC3318664
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.07091-11
Interleukin-27 inhibits vaccine-enhanced pulmonary disease following respiratory syncytial virus infection by regulating cellular memory responses
Abstract
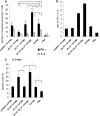
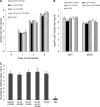
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most important cause of lower respiratory tract disease in young children. In the 1960s, infants vaccinated with formalin-inactivated RSV developed a more severe disease characterized by excessive inflammatory immunopathology in lungs upon natural RSV infection. The fear of causing the vaccine-enhanced disease (VED) is an important obstacle for development of safe and effective RSV vaccines. The recombinant vaccine candidate G1F/M2 immunization also led to VED. It has been proved that cellular memory induced by RSV vaccines contributed to VED. Interleukin-27 (IL-27) and IL-23 regulate Th1, Th17, and/or Th2 cellular immune responses. In this study, mice coimmunized with pcDNA3-IL-27 and G1F/M2 were fully protected and, importantly, did not develop vaccine-enhanced inflammatory responses and immunopathology in lungs after RSV challenge, which was correlated with moderate Th1-, suppressed Th2-, and Th17-like memory responses activated by RSV. In contrast, G1F/M2- or pcDNA3-IL-23+G1F/M2-immunized mice, in which robust Th2- and Th17-like memory responses were induced, developed enhanced pulmonary inflammation and severe immunopathology. Mice coimmunized with G1F/M2 and the two cytokine plasmids exhibited mild inflammatory responses as well as remarkable Th1-, suppressed Th2-, and Th17-like memory responses. These results suggested that Th1-, Th2-, and Th17-like memory responses and, in particular, excessive Th2- and Th17-like memory responses were closely associated with VED; IL-27 may inhibit VED following respiratory syncytial virus infection by regulating cellular memory responses.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RSV recombinant candidate vaccine G1F/M2 with CpG as an adjuvant prevents vaccine-associated lung inflammation, which may be associated with the appropriate types of immune memory in spleens and lungs.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(11):2684-2694. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1596710. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31021703 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide Inhibits FI-RSV Vaccine-enhanced Inflammation Through Regulating Th Responses.Curr Med Sci. 2019 Jun;39(3):363-370. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2044-0. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Curr Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31209804
-
Long-lasting balanced immunity and protective efficacy against respiratory syncytial virus in mice induced by a recombinant protein G1F/M2.Vaccine. 2007 Oct 16;25(42):7422-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17850930
-
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) evades the human adaptive immune system by skewing the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance toward increased levels of Th2 cytokines and IgE, markers of allergy--a review.Virus Genes. 2006 Oct;33(2):235-52. doi: 10.1007/s11262-006-0064-x. Virus Genes. 2006. PMID: 16972040 Review.
-
Understanding respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine-enhanced disease.Immunol Res. 2007;39(1-3):225-39. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0071-6. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917067 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of IL-27 in HSV-1-Induced Herpetic Stromal Keratitis.J Immunol. 2023 Aug 1;211(3):474-485. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200420. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37326494 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory cytokine function in the respiratory tract.Mucosal Immunol. 2019 May;12(3):589-600. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0158-0. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Mucosal Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30874596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro model for the assessment of human immune responses to subunit RSV vaccines.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 19;15(3):e0229660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229660. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32191728 Free PMC article.
-
CpG in Combination with an Inhibitor of Notch Signaling Suppresses Formalin-Inactivated Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Enhanced Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation by Inhibiting Th17 Memory Responses and Promoting Tissue-Resident Memory Cells in Lungs.J Virol. 2017 Apr 28;91(10):e02111-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02111-16. Print 2017 May 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28275186 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Ligand Delta-like 4 Promotes Regulatory T Cell Identity in Pulmonary Viral Infection.J Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;198(4):1492-1502. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601654. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28077598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta-Rodriguez EV, et al. 2007. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat. Immunol. 8:639–646 - PubMed
-
- Artis D, et al. 2004. The IL-27 receptor (WSX-1) is an inhibitor of innate and adaptive elements of type 2 immunity. J. Immunol. 173:5626–5634 - PubMed
-
- Bermejo-Martin JF, et al. 2007. Persistence of proinflammatory response after severe respiratory syncytial virus disease in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119:1547–1550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

