Injectable drug-eluting elastomeric polymer: a novel submucosal injection material
- PMID: 22301346
- PMCID: PMC3334415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.12.009
Injectable drug-eluting elastomeric polymer: a novel submucosal injection material
Abstract
Background: Biodegradable hydrogels can deliver therapeutic payloads with great potentials in EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) to yield improvements in efficacy and foster mucosal regeneration.
Objective: To assess the efficacy of an injectable drug-eluting elastomeric polymer (iDEEP) as a submucosal injection material.
Design: Comparative study of 3 different solutions by using material characterization tests and ex vivo and in vivo porcine models.
Setting: Academic hospital.
Interventions: Thirty gastric submucosal cushions were achieved with saline solution (0.9%), sodium hyaluronate (0.4%), and iDEEP (n = 10) in ex vivo porcine stomachs. Four porcine gastric submucosal cushions were then created in vivo by using iDEEP.
Main outcome measurements: Maximum injection pressure, rebamipide release rate, submucosal elevation duration, and assessment of in vivo efficacy by en bloc resection.
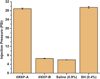
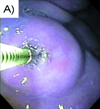
Results: No significant difference in injection pressures between iDEEP (28.9 ± 0.3 psi) and sodium hyaluronate (29.5 ± 0.4 psi, P > .05) was observed. iDEEP gels displayed a controlled release of rebamipide up to 2 weeks in vitro. The elevation height of iDEEP (5.7 ± 0.5 mm) was higher than that of saline solution (2.8 ± 0.2 mm, P < .01) and sodium hyaluronate (4.2 ± 0.2 mm, P < .05). All EMR procedures were successfully performed after injection of iDEEP, and a large gel cushion was noted after the resection procedure.
Limitations: Benchtop, ex vivo, and nonsurvival pig study.
Conclusions: A novel injection solution was evaluated for endoscopic resection. These results suggest that iDEEP may provide a significant step toward the realization of an ideal EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection injection material.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest to disclose
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rebamipide solution: a novel submucosal injection material to promote healing speed and healing quality of ulcers induced by endoscopic submucosal dissection.Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Apr;87(4):1114-1120. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.09.040. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018. PMID: 28993136
-
Efficacy of a reverse-phase polymer as a submucosal injection solution for EMR: a comparative study (with video).Gastrointest Endosc. 2009 May;69(6):1135-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.07.032. Epub 2009 Jan 18. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009. PMID: 19152883
-
Efficacy and safety of SIC-8000 (Eleview®) for submucosal injection for endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection in an in vivo porcine model.Dig Liver Dis. 2018 Mar;50(3):260-266. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.11.017. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Dig Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 29396133
-
Application of hydrogels as submucosal fluid cushions for endoscopic mucosal resection and submucosal dissection.J Artif Organs. 2015 Sep;18(3):191-8. doi: 10.1007/s10047-015-0843-z. Epub 2015 May 23. J Artif Organs. 2015. PMID: 26001772 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) plus rebamipide for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcers: a meta-analysis.Intern Med. 2014;53(12):1243-8. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.2160. Epub 2014 Jun 15. Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24930641 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) in Colorectal Tumors.Viszeralmedizin. 2014 Feb;30(1):39-44. doi: 10.1159/000358529. Viszeralmedizin. 2014. PMID: 26288580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellulose nanofiber dispersion as a new submucosal injection material for endoscopic treatment: preliminary experimental study.Endosc Int Open. 2020 May;8(5):E623-E627. doi: 10.1055/a-1119-6387. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Endosc Int Open. 2020. PMID: 32355880 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection and its potential role in the management of early colorectal neoplasia in UK.Frontline Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr;7(2):129-134. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2014-100434. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 28839847 Free PMC article.
-
A review of hydrogels used in endoscopic submucosal dissection for intraoperative submucosal cushions and postoperative management.Regen Biomater. 2023 Jun 22;10:rbad064. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbad064. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37501677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rebamipide delivered by brushite cement enhances osteoblast and macrophage proliferation.PLoS One. 2015 May 29;10(5):e0128324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128324. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26023912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, et al. Comparison of various submucosal injection solutions for maintaining mucosal elevation during endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 2004;36:579–583. - PubMed
-
- Kantsevoy SV, Adler DG, Conway JD, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto H, Yube T, Isoda N, et al. A novel method of endoscopic mucosal resection using sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;50:251–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

