Structural and functional characterization of a novel nonglycosidic type I NKT agonist with immunomodulatory properties
- PMID: 22301545
- PMCID: PMC3288653
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103049
Structural and functional characterization of a novel nonglycosidic type I NKT agonist with immunomodulatory properties
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2012 Oct 15;189(8):4194. Alari-Pahisa, Elisenda [corrected to Alari-Pahissa, Elisenda]
Abstract
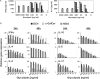
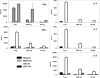
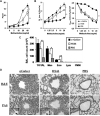
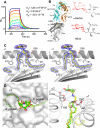
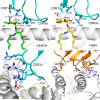
Activation of type I NKT (iNKT) cells by CD1d-presented agonists is a potent immunotherapeutic tool. α-Galactosylceramide (α-GalCer) is the prototypic agonist, but its excessive potency with simultaneous production of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines hampers its potential therapeutic use. In search for novel agonists, we have analyzed the structure and function of HS44, a synthetic aminocyclitolic ceramide analog designed to avoid unrestrained iNKT cell activation. HS44 is a weaker agonist compared with α-GalCer in vitro, although in vivo it induces robust IFN-γ production, and highly reduced but still functional Th2 response. The characteristic cytokine storm produced upon α-GalCer activation was not induced. Consequently, HS44 induced a very efficient iNKT cell-dependent antitumoral response in B16 animal model. In addition, intranasal administration showed the capacity to induce lung inflammation and airway hyperreactivity, a cardinal asthma feature. Thus, HS44 is able to elicit functional Th1 or Th2 responses. Structural studies show that HS44 binds to CD1d with the same conformation as α-GalCer. The TCR binds to HS44 similarly as α-GalCer, but forms less contacts, thus explaining its weaker TCR affinity and, consequently, its weaker recognition by iNKT cells. The ability of this compound to activate an efficient, but not massive, tailored functional immune response makes it an attractive reagent for immune manipulation.
Figures

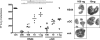
References
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Castano AR, Segelke BW, Stura EA, Peterson PA, Wilson IA. Crystal structure of mouse CD1: An MHC-like fold with a large hydrophobic binding groove. Science. 1997;277:339. - PubMed
-
- Zajonc DM, Kronenberg M. Carbohydrate specificity of the recognition of diverse glycolipids by natural killer T cells. Immunol Rev. 2009;230:188. - PubMed
-
- Zhou D, Mattner J, Cantu C, 3rd, Schrantz N, Yin N, Gao Y, Sagiv Y, Hudspeth K, Wu YP, Yamashita T, Teneberg S, Wang D, Proia RL, Levery SB, Savage PB, Teyton L, Bendelac A. Lysosomal glycosphingolipid recognition by NKT cells. Science. 2004;306:1786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

